Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
The One Device (The Secret History of the iPhone)
Author: Brian Merchant
Narration by: Tristan Morris

Brian Merchant (Author, American technology journalist, writes for The New York Times, Wired, Slate, The Atlantic, and the Guardian.)
Brian Merchant works around the tech world but never quite in it. His understanding of today’s technology has made him a popular writer for national news outlets. Never having been employed by a tech company, his analysis of iPhone history, the role of Jobs, and the history of its development is as an outsider to the process of invention. As a writer about technology, there is a level of objectivity but also reservation about an outsider’s details. Merchant reports what others tell of iPhone’s history rather than as a person being there as a part of its development.

Merchant’s investigation explains the iPhone’s creation is a messy human process entailing the dangers of mining, involvement of other companies and individuals, patent questions, and labor struggles. The impact of the iPhone’s invention is world changing. In a fundamental way, Merchant discounts the mythology of iPhone’s invention by one person or company. There were decades of prior invention before the iPhone became more than an idea, let alone a world changing device.

The scope of manufacturing iPhones made Foxconn the leading international labor subcontractor in the world. Foxconn is estimated to employ 800,000 employees in China alone. Many have been contracted by Apple for iPhone product assembly.
The mining industry and assembly line development were in place before the raw material and labor that would be needed for iPhone development. Merchant suggests Apple became the central orchestrator rather than singular inventor of the iPhone. Merchant argues the iPhone is a synthesis of decades of technological improvement, unnamed engineers, labor and organizations of miners and factory workers, and innovations needed to produce Apple’s revolutionary product.
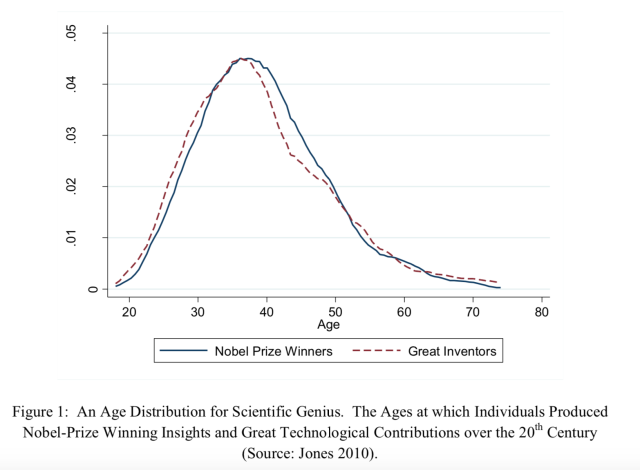
Genius and invention go hand in hand. However, Merchant explains in the early 20th century, much of the technology that became a part of the iPhone’s foundation were already invented. He notes touchscreens, voice recognition tools, motion tracking, and early iterations of what became Artificial Intelligence had already been discovered. Merchant’s intent is not to diminish the genius of Apple, Jobs, or its employees but to show the public that every extraordinary human invention has precursors and essential earlier discoveries. It took Apple’s leadership and employees to integrate the many technologies that had been discovered earlier to create what has become a handheld window to the world. Merchant explains no great inventions are created out of thin air. He suggests every invention of the present is dependent on thought, labor, experience, and invention of the past.
Thomas Kuhn suggests every revolution in science begins with a paradigm in conjunction with discoveries of the past.

Merchant discounts the idea of the “lone genius” because every genius depends on insight and events of the past to correlate what she/he invents in the present. The iPhone unifies decades of technological progress. The iPhones’ invention reorganizes global behavior, creates a new economic and industrial model, and gives the world a pocket supercomputer. The geniuses of Apple earned their reputations, but they relied on discoveries of the past.



Thinking of Curie, Einstein, Newton, and other giants of science, one wonders how Merchant’s belief about genius is valid. He would argue the brilliance of Curie, Einstein, and Newton are built on prior knowledge, their predecessors, and the tools of their time. Their genius is in connecting past knowledge and discovery of others with the present. Their genius is dependent on predecessors. Merchant is not diminishing Jobs’ or Apple’s genius, but their breakthroughs could only come from groundwork established by others.


Like all world changing inventions and discoveries, iPhone came with costs ranging from children’ and adults’ addiction, to rare minerals depletion, to environmental pollution. The long-term effect of iPhones has changed the world with unexpected, often unforeseen, consequences.