Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
The Great Courses: “Mysteries of Modern Physics: Time”
By: Sean Carroll
Lectures by: Sean Carroll

Sean Michael Carroll (American theoretical physicist and philosopher specializing in quantum mechanics, cosmology, and philosophy of science.)
Sean Carroll presents scientists’ views of time, entropy, and life. There are instances of his lectures that are too obscure for this reviewer, but for physicists the lectures are undoubtedly clearer and more concise than for this seeker of understanding.



Carroll explains there are four physical dimensions in the world. There is length, width, depth, and a fourth dimension called time. The first three are easy to understand because they are physical characteristics while time is not. Time cannot be seen, touched, or tasted.

Time is a fourth dimension measured by calendars and clocks that divide the past and present into days, hours, minutes, and seconds. Carroll notes knowledge of length, width, and depth are of the past and present while time points to an unknown future as well as the present and past. Einstein refined the definition of time by renaming it space time which combines physical dimensions with observers’ perception of events, i.e., where and when observations occur and where the observer is located. The significance of Einstein’s space time is that the location and traveling speed of the observer affects the perceived time of events. Carroll’s attention is about time as an arrow that only points forward. Carroll explains how events of the present and past can be defined while the future is unknown. An extended meaning of the arrow of time is that it seems unlikely (though not impossible according to Carroll and the current state of physics) that we can physically return to a past.

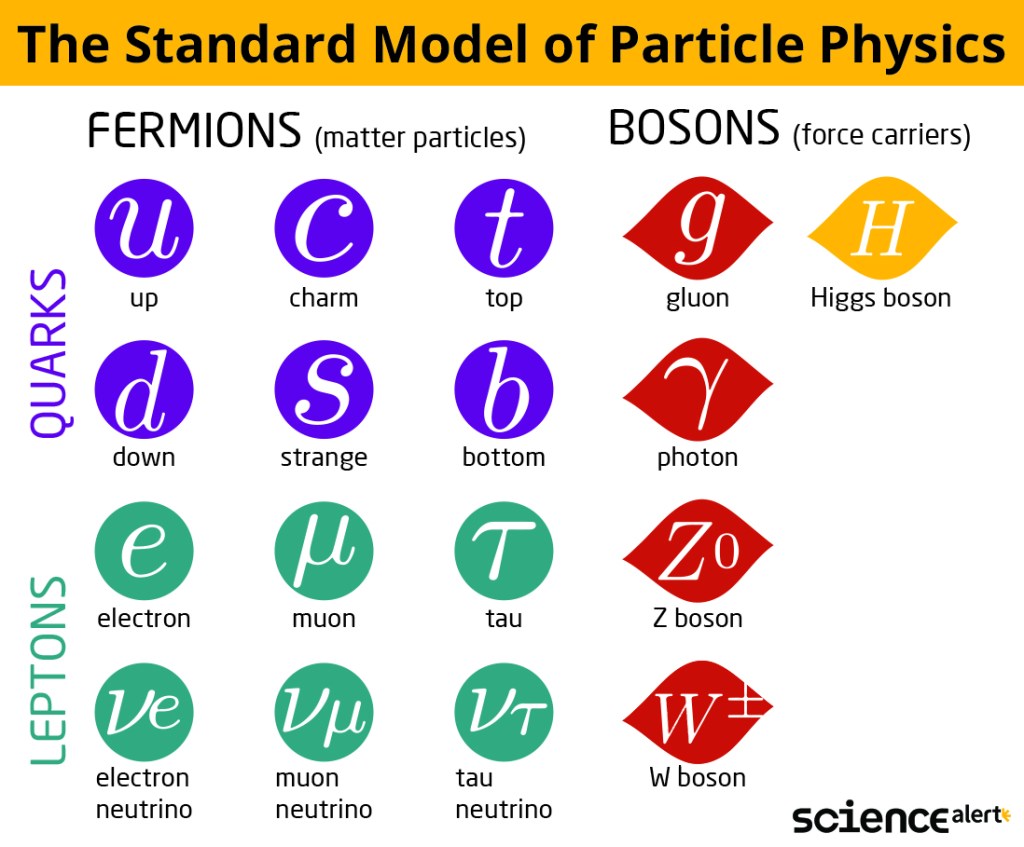
There is a significant distinction between entropy and loss of energy. Energy is always conserved but it may not be useable for work. Entropy is about increased disorder and randomness of energy states. Carroll defines entropy as a characteristic of matter in the world which is in a state of molecular disorder, randomness, and uncertainty. This definition is reinforced by the discovery of quantum mechanics which experimentally illustrates probabilities rather than certainty at atom-level interactions. (Einstein never accepted quantum mechanics as a truth of life but only a step of discovery in physics. Einstein believed there would be a discovery that incorporates quantum mechanics in an ultimately predictive physics world.) Carroll notes a theory that explains gravity along with the proof of quantum mechanics holds a key to whether Einstein is wrong when he suggested God does not play with dice.

An interesting note by Carroll is that transition from low to high entropy has an interesting effect in an experiment with two separate enclosures that are connected. One has gas molecules in it while the other does not. There is a hole between the enclosures through which molecules can enter. Over time the two boxes will have the same amount of gas through a process of equilibration. This reinforces the idea of conservation of energy while demonstrating energy transformation.
Transformation of energy is exhibited in animal life by its eventual death, but Caroll explains it equally applies to all matter in the universe. The idea of entropy is reinforced by the arrow of time that only points in one direction.
At an atomic level, all matter transforms over time.
Entropy does not mean loss of energy. Energy is always conserved but it may not have a useful work purpose. The second law of thermodynamics, postulated by Rudolf Clausius in the 1850s, explains that heat always flows from hotter to colder through the process of entropy. For example, a low-level heat energy may not serve a work purpose, but it still conserves energy balance. Raising the heat on a cube of ice transforms its molecules from a frozen state to water to steam which conserves energy that can generate working steam molecules to power an engine.
Much of Caroll’s lectures are an examination of Ludwig Boltzmann’s theory of statistical mechanics and kinetic theory. Much of Boltzmann’s contribution revolves around the concept of entropy and a detailed understanding of the behavior of particles in gases, liquids, and solids. He performed experiments that proved the conservation of energy and the equilibration of atoms and molecules as an observable phenomenon.
Boltzmann speculated that in the beginning of the universe, the chaotic activity of its beginning transformed into a lower state of entropy to create what we see in the world.


Ludwig Edward Boltzmann (1844-1906, Austrian physicist and philosopher.)
Boltzmann’s idea came before the theory of the Big Bang. The idea of the Big Bang actually presumes less entropy rather than more before the creation of the universe. Boltzmann’s idea is that the universe began in chaos (high entropy) to form what became known as a Boltzmann brain (low entropy), a thought experiment where a highly advanced brain formed in a void, from which the universe evolved. The Boltzmann brain is like the singularity of the Big Bang where cosmic dust condensed into a low entropy state and then exploded into our universe.
The origin of the universe may, in one sense, come from either a Boltzmann brain or a Big Bang. Both suggest the universe began in a low entropy state.

However, the Big Bang seems more reliably built on evidence by the measurement of an expanding universe with proven remnants (cosmic radiation) from a massive explosive event. Either theory implies the potential for a multiverse that began from a low entropy theory of our universe’s origin.
At this point in Carroll’s lectures, one’s head begins to hurt. He addresses the many ramifications of the origin of life. As one gets older, the principle of entropy takes on a personal meaning. Getting older may make one wiser but not smarter.