Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
Mad, Bad, Dangerous to Know
Author: Colm Tóibín’s
Narrated By: Colm Tóibín

Colm Tóibín (Author, Booker Prize winner in 2006, journalist, essayist and short story writer.)
“Mad, Bad, Dangerous to Know” as an audiobook is a bit difficult to understand because of Colm Tóibín’s Irish accent but as one adjusts to its cadence and inflexion, it offers interesting information about the families of Oscar Wilde, W.B. Yeats, and James Joyce.
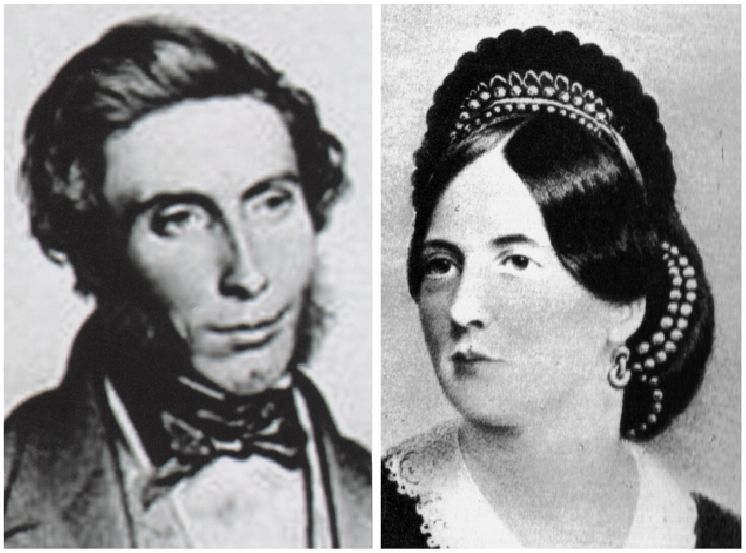

William and Jane Wilde (Parents of Oscar Wilde.)
William Wilde, the father of Oscar, is an important figure in Victorian Ireland. He was a renowned eye-and-ear surgeon who aided the medical profession by compiling statistical information about diseases and mortality of medical treatments as a gauge for human health. His wife, Jane Wilde (pen name-Speranza) was a nationalist poet and political writer. Some characterized her as a radical in comparison to her establishment husband.
Jane Wilde’s husband is accused of sexual misconduct in the treatment of a young female patient in his practice. Mary Travers had accused Dr. Wilde of drugging and seducing her when seeking help for a medical problem. Dr. Wilde is indirectly drawn into court to settle a lawsuit filed by the female patient’s father because of a publicly exposed letter by Jane Wilde about Ms. Travers. The court finds that Dr. Wilde’s wife libeled Ms. Travers in a publicly exposed letter that criticizes her sexual assault claim. The court found Jane Wilde guilty of libel and awarded Travers a symbolic sum of 2 pounds for public humiliation.

In the 19th century, Eibhear Walshe writes a book about the trial brought against Jane Wilde for libelous comments about the sexual abuse of Ms. Travers.
Though Oscar’s father never faced criminal prosecution, his reputation and standing in the community declined. Despite the blow to Dr. Wilde’s reputation, Tóibín argues Ireland’s medical profession benefited from William Wilde’s statistical analysis of medical practice in 19th century Ireland. Nevertheless, the Travers’ trial infers gender discrimination was then and remains a serious problem in modern times.

The Travers’ trial reminds one of gender discrimination in modern times.
Oscar Wilde (1854-190o, the son of Dr. Wilde and Jane Wilde died at the age of 46, Oscar Wilde was an Irish author, poet, playwright who wrote “The Picture of Dorian Gray”. He became famous in London and around the world, convicted in 1895 for gross indecency for homosexual acts.)


John Butler Yeats (1839-1922, W.B. Yeat’s father.)
The next family examined by the author is John Butler Yeats. Little is said about J.B.’s mother but his father was an aspiring portrait artist. This is an equally interesting story. J.B. is characterized as an artist but with a gift of gab and an interesting philosophy of life. John Butler Yeats is identified as a procrastinator that often started painting a portrait but as often failed to finish it. He and his wife had four children, i.e. two girls and two boys. Each contributed to Irish cultural life. Jack, their first son, became one of Ireland’s most celebrated painters. He also illustrated books and wrote plays and novels. He painted in the expressionist style. Susan Mary Yeats was a leader in the Arts & Crafts movement in Ireland. She co-founded the Cuala Press that published works by W.B. and other writers. She helped revive Irish decorative arts but was overshadowed by the brothers. Elizabeth Yeats was a co-founder of the Cuala Press. A little research shows the children had some formal education but as Tóibín suggests, with the exception of W.B.’s formal training at the Metropolitan School of Art in Dublin, the other 3 children were largely self-trained in art, writing, and Irish crafts.
Tóibín shows W.B. had a somewhat rocky relationship with his father when he was younger, but it evolved into a respect for his father’s philosophical view of the world.

When his father lost his wife, he chose to move to New York. Tóibín explains John Butler Yeats was more than a portrait artist. Though he was undisciplined in completing his artistic works, he scraped by with the help of his children’s support. John Yeats had attended Trinty College in Dublin studying the Classics and Law. He used that education to write letters to his children and friends after he moved to New York. The author infers some of W.B.’s poetry is based on ideas gleaned from his father’s philosophical musings. Tóibín notes several books have been published that compiled many of W.B.’s letters.

Rosa Butt portrait painted by J. B. Yeats.
Tóibín characterizes John Butler Yeats as emotionally and financially unreliable but a deeply influential father in W.B.’s life. J.B. exposes W.B. Yeats to the aesthetic and intellectual currents of the time. Tóibín infers J.B. had an extramarital affair with Rosa Butt. Ms. Butt was an acquaintance J.B. made when he painted a portrait of her in his studio. J.B. wrote many letters to Ms. Butt that reflect on his emotional attachment. However, he never returns to Ireland despite many intimations that he would. John Butler Yeats dies on February 34, 1922, in New York City. He was 82 years old, living in a boarding house at 317 West 29th Street. As true to his habits in life, he is said to have died with an unfinished self-portrait beside his bed. He is buried in Chestertown Rural Cemetery in Chestertown, New York.

James Joyce, leaning on his mother, with his father at the right (John Stanislaus Joyce).
John Stanislaus Joyce (1849-1931, died at the age of 82

The final chapters of Tóibín’s book are about James Joyce’s family. His father is John Stanislaus Joyce. Tóibín suggests James had an ambivalent opinion of fathers and particularly his own father. John Joyce is characterized as an abusive, alcoholic husband, and incompetent manager of his inheritance. With ten children and a wife, John Joyce loses his inheritance and effectively drives his son away from Ireland. James is the oldest, born in 1882. Tóibín explains that his voice and personality are ever present in James Joyce’s famous characters in both “Ulysses” and “A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man“. Both books take a dim view of fatherhood while exemplifying an erudite father who projects a “man about town” image. However, Tóibín shows John Joyce to be an incompetent money manager and abusive family man.

James Joyce (1882-1941)
In “A Portrait…” Stephen’s biological father is depicted as charming but irresponsible. Like James Joyce’s father, his main character’s father is financially unstable and an emotionally distant, abusive parent. In “A Portrait…” Stephen Daedalus is alienated and chooses a life independent of the Catholic Church because he views it like a surrogate father that imposes moral and spiritual authority without justification.
In “Ulysses”, James Joyces’s main character argues paternity is a fiction while maternity is merely a biological function. At best, one sees James Joyce is ambivalent about his dad. James experiences episodes of camaraderie when socializing with his father as a drinker and as a tenor singing partner. Both are supporters of Parnell, the Irish nationalist leader who supported Home Rule and independence from England.

Tóibín suggests James Joyce’s feelings about his mother are marked by guilt, presumably for not protecting her from her abusive husband but also because of her belief in God and patriarchal authority. In reading Joyce’s works, particularly “A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man” and “Ulysses”, one can see James Joyce’s as a son of a loving, religious mother and abusive father who drank too much. James knew his mother loved him, but his father could not manage his or his family’s welfare.

May Murray Joyce (James Joyce’s mother, 1859-1903, died at the age of 44.)
William Wilde, Jane Wilde, and John Stanislaus Joyce fit the description of “Mad, Bad, Dangerous to Know”. However, John Butler Yeats seems somewhat less dangerous while contributing to the life and intellectual development of W.B. Yeats.