Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
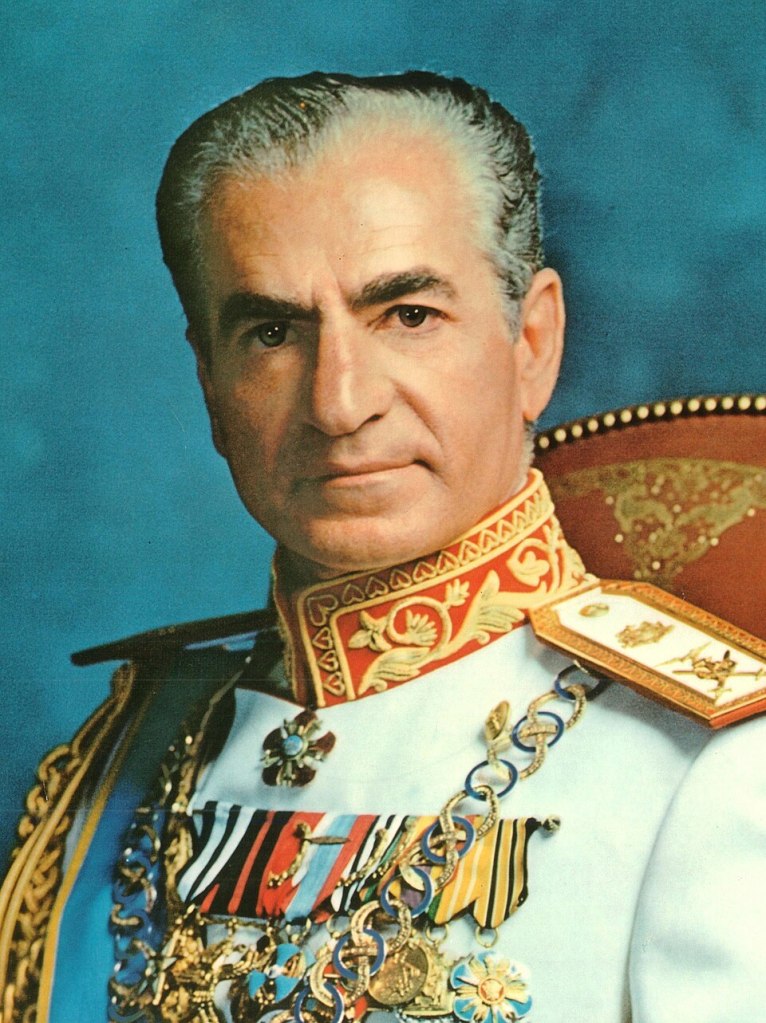
King of Kings (The Iranian Revolution: A Story of Hubris, Delusion and Catastrophic Miscalculation)
Author: Scott Anderson
Narration by: Malcolm Hillgartner & 1 more

Scott Anderson is a novelist and veteran war correspondent. His previous novels include Moonlight Hotel and The Man Who Tried to Save the World.
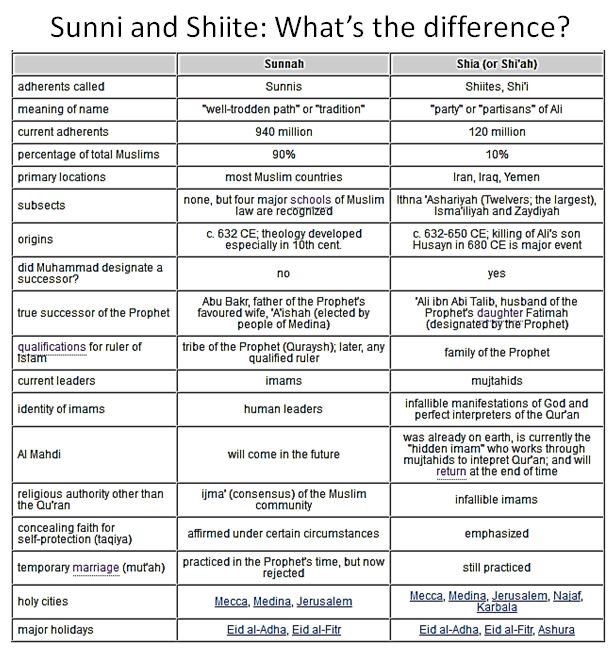
“King of Kings” is an informative historical account of the collapse of Iran as a former monarchy and current theocracy. The hubris of the King and the Ayatollahs have no one to blame but themselves for their government’s failure. What Anderson shows is that what royal and theological leaders have in common. Both neglect the wellbeing of the Iranian people. The King squandered the wealth created by the oil industry to buy a false sense of security. The “King of Kings” made excessive investments in weapons and a spy service called SVAK rather than invest in Iran’s economy for the betterment of its citizens. The King’s SVAK turned into MOIS in the Ayatollah’ regimes. Neither regime invested in the people’s welfare. Both secret services were designed to spy on Iran’s citizens and reinforce the delusion of serving the people when in fact they were designed to preserve their governments’ power and control.
Iran’s leadership as a monarchy and theocracy have failed its people.

Anderson shows the “King of Kings” initially improves the general welfare of Iran’s citizens but because of inept leadership and the privileges of power, the Shah failed the Iranian people. The Shah’s incompetence as a manager of Iran’s great oil wealth is a wasted opportunity that could have provided a better life for its citizens. Rather than encouraging economic growth, the Shah chose to invest in weaponry and other countries products to sustain Iran’s economy.

The Iranian people were not farming or creating their own industries to sustain and grow their economy.
The King’s failure to invest oil revenues in the economy and Ayatollahs who cared little about economic investment, impoverished the Iranian people. When other countries like Saudi Arabia flooded the market with oil, the economy of Iran collapsed. That loss of oil income impoverished the people of Iran. Iran had become dependent on other countries produce rather than the work of their own farmers and industrialists to support their lives and families. That impoverishment drove many back to the ideal of a Muslim religion that believes hardships of life are only preparation for heaven.
The rule of the Ayatollahs seems as incompetent as the Shah’s.

The Ayatollahs fail to improve the economy and rely on a secret service that victimizes all who criticize their rule. It seems they believe the hardship of life is no concern because heaven awaits all those who believe in the Ayatollah’s governance. Anyone who fails to support the Shia Muslim autocracy is murdered or imprisoned based on the Ayatollahs’ belief in the hereafter. Iranians may believe in the Ayatollahs’ teaching and are willing to support their government, but a substantial portion of the Iranian people are discontented with their poverty and hunger.

Iranian oil fields supported the wealth of Iran before Saudi Arabia’s entry into the market.
Anderson explains how Iran became a troubled country. Neither rule as a monarchy or theocracy offered a solution to poverty and hunger. The answer may not be capitalism or democracy, but the present and past Iranian governments have not served the needs of its people. One’s heart goes out to the citizens of Iran and wonders what hope there is for their future. Iran seems trapped between rock and a hard place, a choice between the bombs of war and religious fundamentalism.