Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
38 LONDRES STREET (on Impunity, Pinochet in England, and a Nazi in Patagonia)
Author: Phillip Sands
Narration by: Phillip Sands

Peter Sands (Author, Executive Director of the Global Fund to Fight Aids, Tuberculosis and Malaria, former CEO of Standard Chartered, known as a British Banker.)
Peter Sands book is interesting and a compelling history that would have been clearer if, at the beginning of his book, he had more precisely identified Augusto José Ramón Pinochet Ugarte’s atrocities in Chile. Those atrocities are detailed after one is nearly halfway through the book.
“38 Londres Street” is the address at which torture, illegal detentions and assassinations took place under the leadership of Pinochet. Sands explains 40,000 people were detained or tortured under Pinochet’s regime. 3,000 people were killed or disappeared during Pinochet’s reign. He ruled Chile for 17 years before being arrested in London when a Spanish judge issued a warrant for his arrest for genocide and terrorism. This was the first time a former head of state was charged for a crime by a universal jurisdiction.
Augusto Pinochet (born in 1915-died in 2006. As a military officer and politician, he instituted a military coup to become dictator of Chile from 1978 to 1990.)
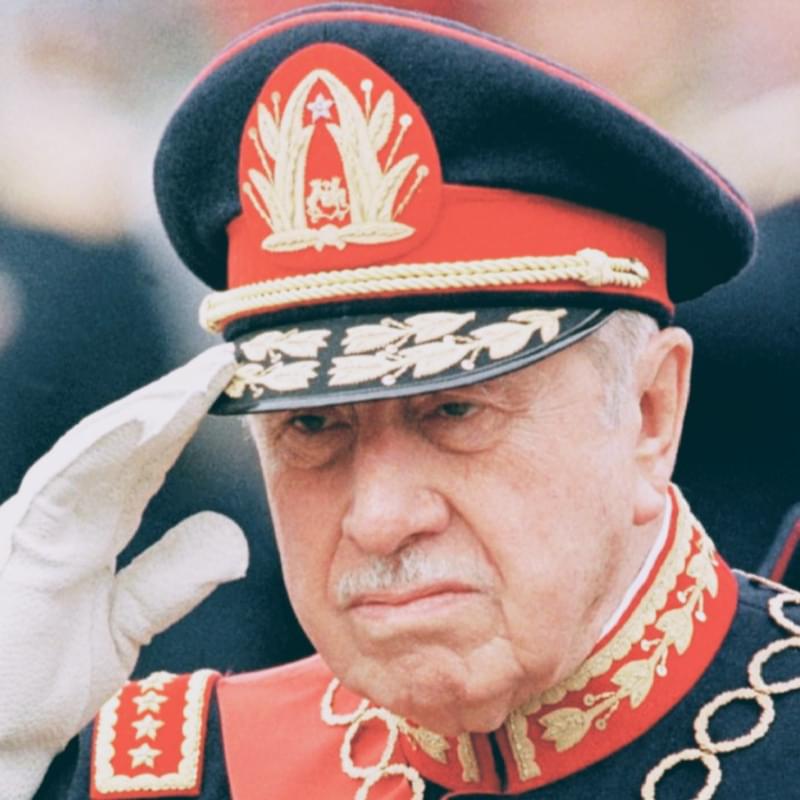


Pinochet became Dictator of Chile when he overthrew President Salvador Allende in 1973.
Because of mining and trade interests in Chile by American and British corporations, along with distrust of Allende’s Socialist Party and Marxist beliefs, Allende was considered an enemy of America’s and Great Britain’s leadership. Allende was often labeled as a Communist because of nationalizing Chile’s copper mines, redistributing land, and increasing wages for less wealthy Chileans.
In truth, Allende rejected the idea of a one-party communist state while believing Chile should gradually become a Democracy. Both America and Great Britain supported Pinochet’s revolution because of their economic interest in trade with Chile and their opposition to his socialist beliefs. Declassified records show the CIA funded opposition parties to destabilize Allende’s government. Because Britain was a close ally of America and had economic interests in Chile, both Nixon and Edward Heath, the Prime Minister of Great Britain, supported Pinochet’s military junta. When Margaret Thatcher became Prime Minister, she also supported Pinochet’s government. In the atmosphere of the cold war, Pinochet’s rebellion seemed in the best interest of America’s and England’s leadership.
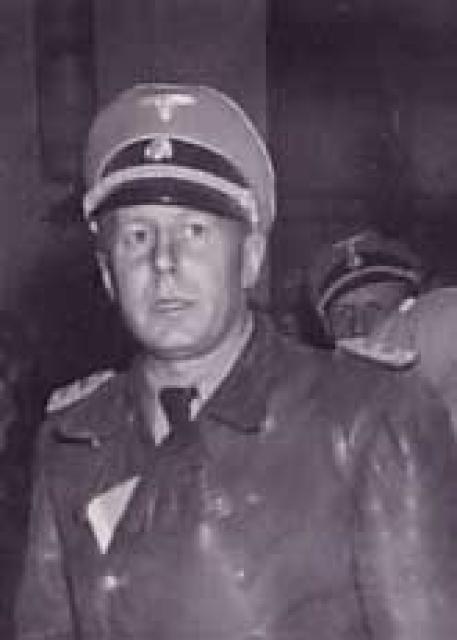


Walter Rauff was a Nazi commander during WWII who escaped justice for exterminating an estimated 100,000 people in gas vans. Rauff designed the vans for Hitler’s occupation of Poland, Russia, and Ukraine. The picture to the right is Rauff as he appeared in Chile as an employee of Pinochet’s government.
The reason for the Chilean coup is not what Phillip Sands is primarily interested in but, as an author and lawyer, he explains the significant change in jurisdictional law with Pinochet’s indictment. It set a precedent for a foreign country’s right to indict another country’s leadership that tortures, disappears, and kills its own citizens.

The most troubling part of his argument for the change in international law is that it seems ineffective when only viewed from the indictment of Pinochet. To find a leader chargeable for genocide is important, but Chile’s protection of death camp SS officers like Walther Rauff reminds one of Putin’s atrocities as President of Russia. Rauff was protected by Pinochet’ government despite his role in Nazi Germany. Sands notes that Rauff assisted Pinochet in Chile’s repressive activities at 38 Londres Street.

Rauff’s disguised ambulances used to gas Jewish citizens and others.
The last half of Sands’ book is about the extensive interviews and research he did on Rauff’s past life. Like Pinochet, Rauff escapes justice and dies of natural causes. However, Jewish Nazi hunters did track down Rauff with the intent of killing him. Sands explains they were unsuccessful despite having knocked on his door before being denied access by a woman who answered the knock.
Magistrate Baltasar Garzón (Former judge of Spain’s central criminal court that set the precedent for universal jurisdiction.)

The world owes Spain gratitude for embracing universal jurisdiction despite its failure to successfully hold Pinochet for his crimes against humanity. That precedent gives weight to the principle of international justice. Magistrate Baltasar Garzón used the Pinochet case to set the precedent that sovereignty does not shield perpetrators of torture and genocide to be free of indictment and its potential for punishment. Adolf Eichmann is brought to justice in 1961 and the survivors of the 2003 massacre in Bolivia were awarded $10 million in damages.
One’s thoughts go to Putin’s incarceration of Navalny, his ordered slaughter of Chechens and his aggressive war against Ukraine. Navalny exposed Putin’s corruption in state-owned companies owned by Kremlin elites, i.e. the same elites that support the war in Ukraine.

Will Putin escape the long arm of the law?
As a professor of international law, Sands gives listener/readers a view of the important precedent of universal jurisdiction with the successful arrest of Pinochet for crimes against humanity. The irony of Sands history of this precedent is that Pinochet is not convicted and returns to Chile in 2000. Pinochet dies in 2006 at age 91. Putin has been indicted by the International Criminal Court for war crimes, unlawful deportation and transfer of Ukrainian children but has not yet faced trial. One suspects President Putin faces the same “slap of the hand” as Pinochet and will die of natural causes without being convicted for his crimes.