Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
BEING JEWISH AFTER THE DESTRUCTION OF GAZA (A Reckoning)
Author: Peter Beinart
Narration by: Malcolm Gladwell
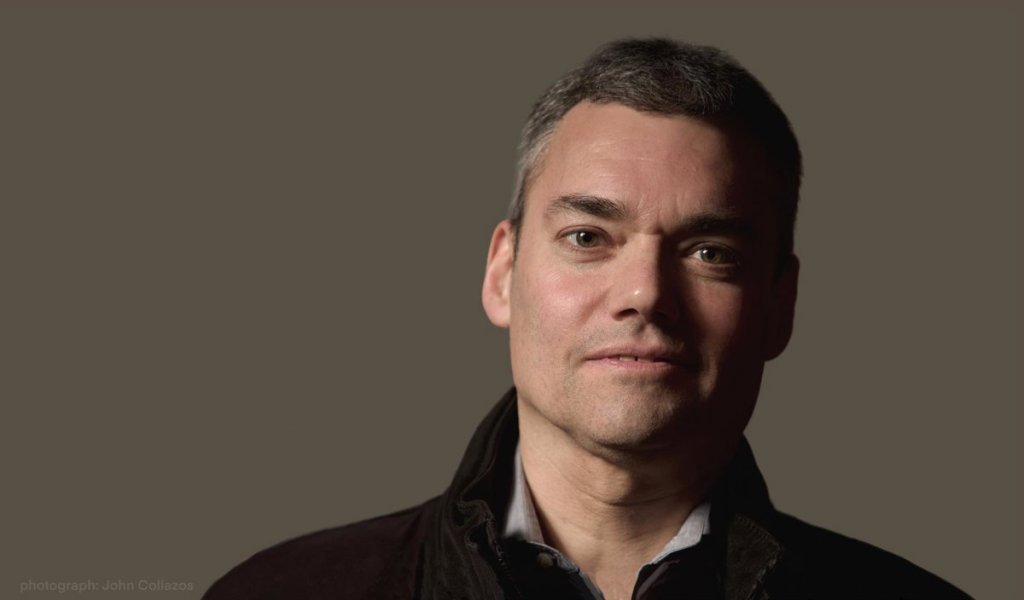

Peter Beinart (Author, journalist, political commentator, professor, former editor of the New Republic, born in Cambridge, Mass. to Jewish immigrants from S. Africa.)
This is a surprising Jewish author’s analysis of Israel’s response to the horror of Hamas’ murders/rapes of 1200 people and the taking of 251 Jewish hostages on October 7, 2023. Peter Beinart appears to be a devout Jew and journalist who criticizes Israel’s response to Hamas’s brutal attack and hostage taking. He believes, as current news reports confirm, Hamas will return to control and influence Gaza and West Bank Palestinians after Israel’s brutal response to the Hamas’ atrocity.
NYT’s Picture of Grief over the Hamas attack on October 7th, 2023.

Without reservation, Beinart condemns Hamas for their war crime on October 7th. However, his book equally condemns Netanyahu’s response. Beinart points to the Israeli government’s destruction, murder, and starvation of thousands of Palestinian men, women, and children who had nothing to do with the planning or execution of the Hamas horror of October 7th. The author argues Israel must focus on a political, non-military solution to Palestinian human rights. He believes Netanyahu’s actions only perpetuate a cycle of violence in Israel which will not achieve security for either the Israeli or Palestinian people.


One wonders how unpopular Beinart’s opinion may be among Israel’s Jewish population. As a blogger who received written comments from a devout Jewish person who supports Trump and Netanyahu’s actions in Israel, it is surprising to hear Beinart’s analysis of the Gaza war and his criticism of Israel’s actions. As the reviewer of this book who admittedly has little respect for religion and its history of atrocities, it is encouraging to hear from one who believes in their religion and condemns those who have no empathy for other religions. God is a universal concept with religions that worship His existence in different ways. Beinart makes one wonder why there is so little room for a “let it be” attitude toward different religious beliefs.

Empathy.
Beinart argues for Jewish empathy toward Palestinians while condemning Hamas’ actions in Israel. He believes long-term peace requires political compromise and a recognition of Palestinian rights. Military actions only guarantee rather than deter future violence and injustice. Beinart’s plan is to end Israeli’ occupation of Gaza and expand the rights of Palestinians to control Gaza and the West Bank. He argues it can be either a one-state or two-state solution. Beinart argues ground invasion by Israel in Gaza must stop. He recommends forthrightly engaging the humanitarian crises in Gaza by providing aid and rebuilding what has been destroyed.

Pursuit of peace is not easy.
None of this is easy because of the enmity that remains. The complications of political opposition, and security are ongoing concerns for Israelites and Palestinians, but Beinart believes the risks of a negotiated political, religious, and territorial settlement is worth it. Human equality is a work in progress for all nations in the world. Beinart persuasively argues a political and territorial agreement between Palestinians and Israelites is the only possible path to peace. Like America’s Civil War and the issues of slavery and independence, peace will only come to Israel with a political and territorial agreement based on human equality. Of course, the drive for equality remains a work in progress for America. That will be true in Israel for generations to come, but peace can be restored with pursuit of equality for Palestinians and Jews.