Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
The Man Who Loved China (The Fantastic Story of the Eccentric Scientist Who Unlocked the Mysteries of the Middle Kingdom)
Author: Simon Winchester
Narration by: Simon Winchester

Simon Winchester (Author, historian, British American author, journalist, and broadcaster.)
Having traveled to China a few years ago, it is interesting to listen to Simon Winchester’s biography of Joseph Needham, who is considered one of the foremost historians of Chinese science and technology.
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham (1900-1995, British biochemist, historian of science and sinologist who wrote a history of Chinese science and technology based on his British education and experience in China during the 1940s.)

Discovery of the new can improve or impede society. In listening to this biography of Joseph Needham, one wonders how farther ahead science might be if it was more widely shared between countries of the world. Needham is characterized as a polymath who became educated as a biochemist at Cambridge. Needham is a freethinking eccentric, a nudist, a folk dancer, and a thoroughly unconventional human being.
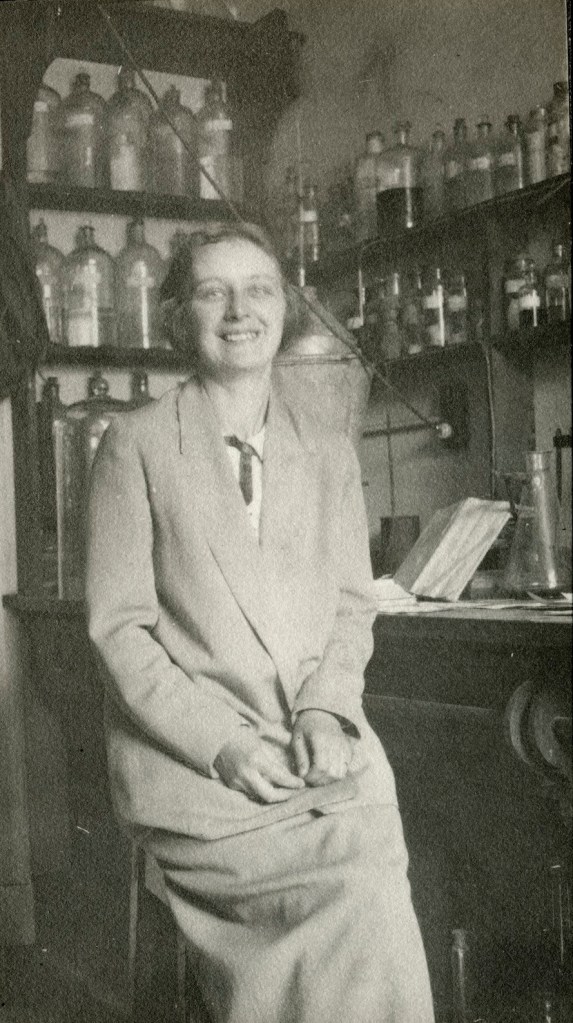
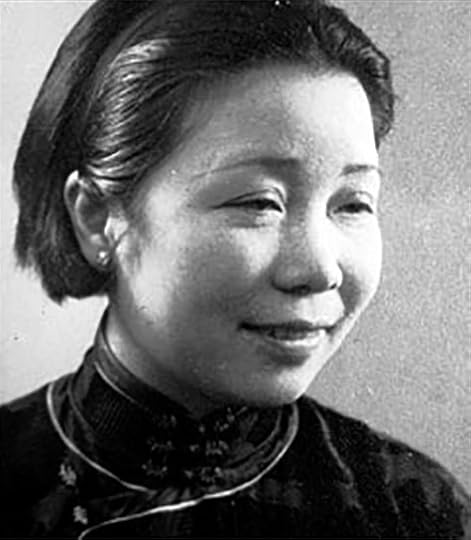


Needham meets a fellow student at Cambridge with whom he pursues a scientific/intellectual partnership and an “open” marriage that lasts until the death of his wife in 1987. Needham’s first wife, Dorothy Moyle Needham, offers stability to his life while accepting a second woman, Lu Gwei-djen, as an intimate in Needham’s life during their marriage. Dr. Gwei-djen was also a biochemist who studied at Cambridge. When Needham’s wife dies in 1987, after 63 years of marriage, he marries Lu Gwei-djen.
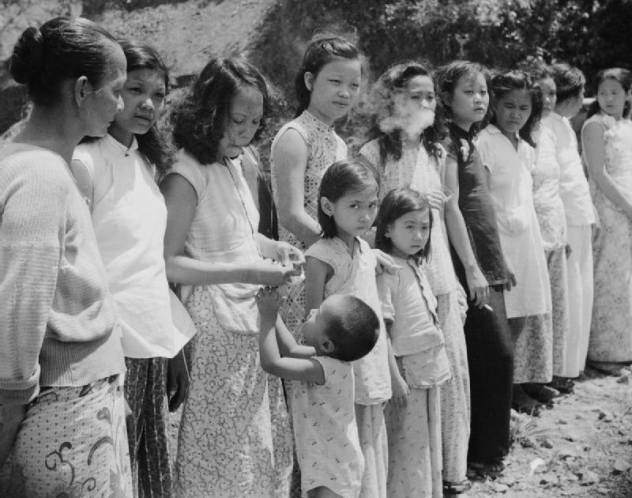

Japan creates what is misogynistically characterized as “comfort women” in their attack and domination of China in the early years of WWII.
As WWII began and the Japanese were attacking China, Needham is engaged by the Sino-British Science Cooperation Office to document scientific manuscripts, meet Chinese scholars, and build a record of China’s scientific networks. His wife joins Needham in 1944 just before Needham’s return to Great Britain. Needham’s separation from his wife gave him time to become an important historian of Chinese Science. His grasp of the Chinese language from his association with Lu Gwei-djen is a great aid to his accumulation of China’s extraordinary advances in science that created many discoveries–long before the rest of the world.


Needham fell in love with China and became acquainted with the war years of China and its communist movement. Needham looked favorably on the communist philosophical movement. However, his political leanings were inconsequential because his primary focus is on China’s scientific history.

Early discoveries in China.
Needam’s research results in a book titled “Science and Civilization in China”. With the help of Lu Gwei-djen, his book became a societal corrective to the West’s bias about China’s technological backwardness. Needam reveals amazing discoveries made by China long before the rest of the world. He found papermaking is developed in the 2nd century BCE, the magnetic compass was used in China in the 11th century, gunpowder is discovered in the 9th century, and printing began in the 7th century. Adding to these discoveries are the many engineering and mechanical innovations of China. They discovered the value of differential gears to aid vehicle function, the idea of a sternpost to guide ships, water power to aid clockworks with escapements for timekeeping.

Agricultural invention in early China.
Needham discovers the agricultural and industrial breakthroughs of China. They used multi-tube seed drills and advanced iron plows to improve agricultural yields centuries before European innovations. Between the 5th and 3rd century BCE, China had developed blast furnaces and iron-working innovations that were not discovered in the west until the medieval period. The Song dynasty in the 10th century pioneered the use of paper money backed by the government.
Silk making in early China.
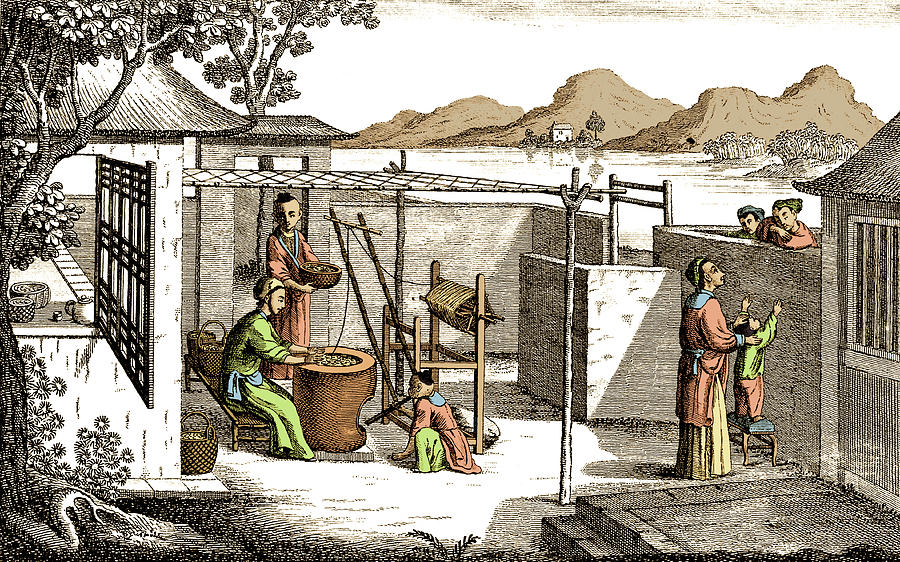

In the science of chemistry, silk production began thousands of years before the west understood its value. Porcelain innovation with hardening through a high-temperature process was used long before its discovery in Europe in the 18th century. Natural gas drilling was discovered with the invention of bamboo derricks and piping for industrial use. Chinese gas drilling dated back to when Roman legions were invading Europe.
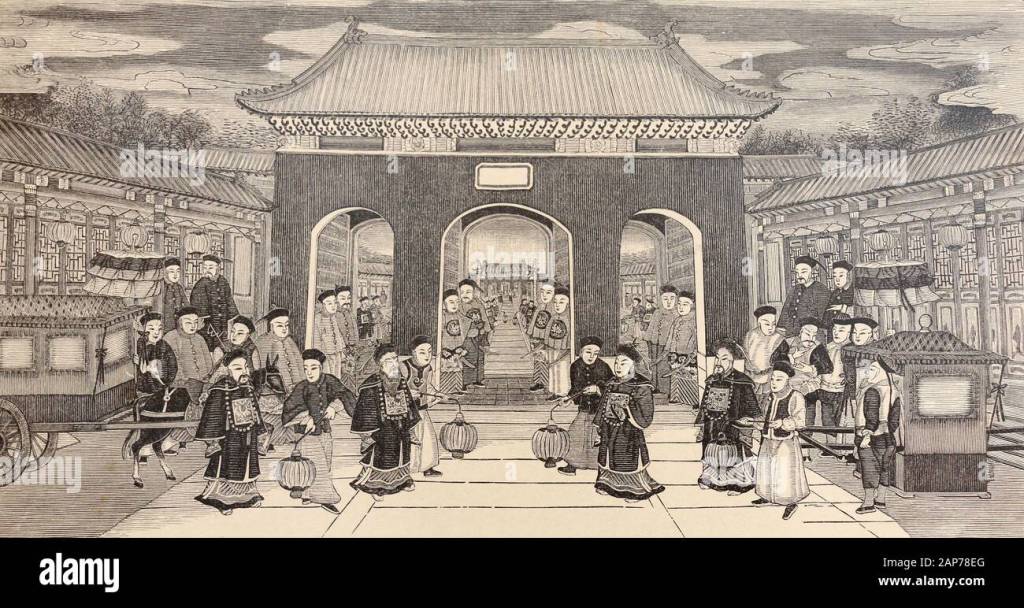

China’s centralized bureaucracy.
What is puzzling about Needham’s book is not only how early these discoveries were made in China, but why these remarkable innovation capabilities did not continue through the twentieth century. He argues the foundation of their advances is its powerful, centralized bureaucratic state, a culture that valued practical knowledge, and a worldview that is comfortable with pattern, process, and observation of nature.
Management of China’s waterways is critical for agriculture and flood risk to those who lived near rivers. Life experience with the threats and benefits of water demanded Chinese attention. Literacy and standardized examinations in China created a cadre of technically motivated officials. With systematic observation of nature, these technocrats harnessed the power of water. So why has there been nothing like the scientific revolution that happened in Europe. To this reviewer, something changed with the rise of communism.

China’s education system.
Needham’s book argues the bureaucracy of China became too conservative and discouraged independent initiatives while emphasizing stability through exam-driven education. Conformity became more important than innovation. Needham infers the scientific revolution went into hibernation in China while blossoming in Europe. One may speculate that is partly due to emphasis on communism, a socio/political rather than a science/nature focused view of life, i.e. a view toward social stability more than one of curious exploration,
CHINA
Winchester’s biography of Needham offers valuable insight to scientific discovery and its intersection with socio/political structure of government. Government bureaucracy can either aid or impede nation-state’ discovery and innovation.