Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
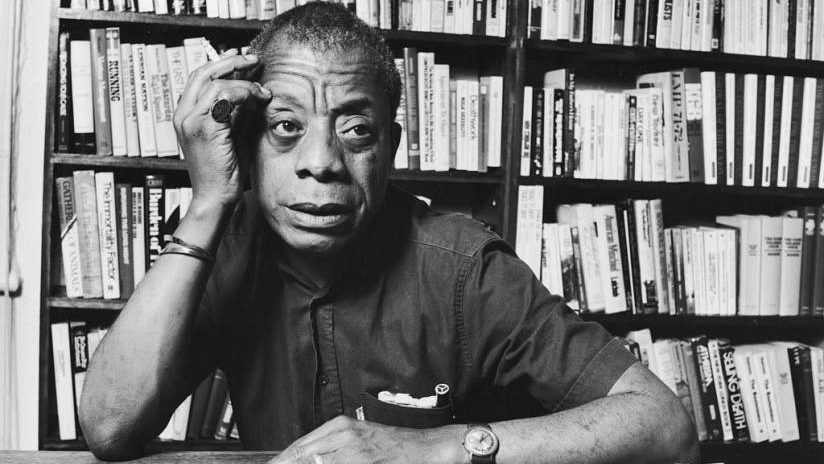
BALDWIN (A Love Story)
Author: Nicholas Boggs
Narration by: Ron Butler

Nicholas Boggs (Author, born in Washington D.C., a civil rights activist, raised in Cleveland as the son of a civil rights lawyer who was also a music teacher. Received a BA from Yale and PhD in English from Columbia University.)
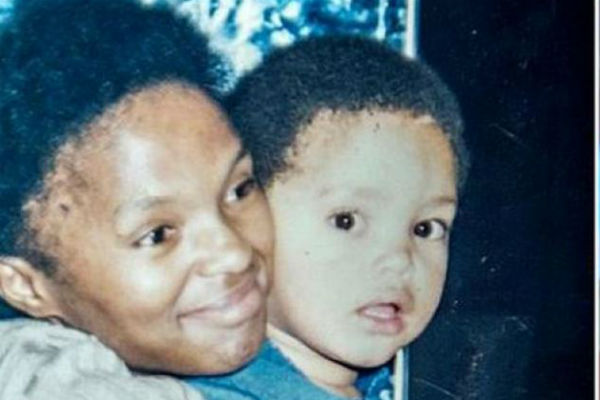
Nicholas Boggs shows why his biography of James Baldwin is “A Love Story”. Baldwin’s difficult life as a young Black American raised in Harlem offers speculative insight to homosexuality and racism. Baldwin grew up with a stepfather he feared. His stepfather was a stern, authoritarian, and abusive man who worked as a Pentecostal preacher who “raised” James from the age of two or three. His stepfather is said to have beaten him, told Baldwin he was ugly and would never amount to anything. His stepfather died in 1943 when James Baldwin was 19 years old, James became caregiver for his mother and eight siblings.
Treavor Noah’s autobiography writes of his abusive stepfather.

As a voracious reader of books and early sexual liaisons, Baldwin leaves Harlem to go to Paris.
As a 24-year-old, Baldwin scrapes enough money together to travel to Paris where he grew to become a great writer, not just another Black American. Despite a stepfather who disliked white people, James grew to overcome physical and mental abuse through belief in God in his youth and belief in humanity as an adult.
In Paris, the 24-year-old Baldwin falls in love with a white 17-year-old youngster who influences his life with experiences that lead to his success as a writer. Lucian Happersberger and Baldwin become life-long friends.
Lucien Happersberger and James Baldwin in their youth.

Having lived in the household of a Pentecostal Preacher, James initially chose to become a preacher. But, at the age of 17, he left the pulpit and rejected belief in God. Boggs infers Baldwin’s pursuit of literature replaced his belief in God because Christianity sanctifies rather than condemns racism. He felt the church was limiting and dogmatic. His stepfather embodied a religion of fear and bitterness that his stepson would not accept.

The themes of “Go Tell It on the Mountain”, Baldwin’s first published book, is about faith, religion, sin, morality, race, racism, gender, patriarchy, and one’s search for identity.
“Go Tell It on the Mountain” is an autobiographical view of life and growth to manhood as a child raised in Harlem. It took ten years to write “…the Mountain”. It released him from the ghost of his stepfather’s cruelty and set the stage for his exploration of race, religion, sexuality, and personal identity.

Beaufort Delaney (Artist who befriended and became a mentor to James Baldwin.)
Boggs identifies four men that had the greatest influence on Baldwin’s life. His mentor becomes Beauford Delaney, a gay Black American painter he met when he was 16 years old. Delaney was 39 when he met Baldwin. Delaney became a major figure in American modernist painting and the Harlem Renaissance in the 1930s and 40s. He introduced Baldwin to life and encouraged him to become an artist. Delany’s homosexuality helped Baldwin deal with his race and sexual orientation. He helped Baldwin believe in himself and put him on a path toward becoming a literary artist. They were friends for forty years when Delaney died in 1979. Baldwin died 8 years later, acknowledging Delaney as his mentor and guide through his tumultuous life.

Lucien Happersberger (On the far left of James Baldwin.)
The success of “Go Tell It on the Mountain” confirmed Baldwin’s reputation as a writer. Baldwin found truth in the books he read and the life he began to live in Paris. At the age of 24, Baldwin left his family in Harlem to become a writer in Paris. In Paris he falls in love with Lucien Happersberger, a 17-year-old white bisexual who became more relevant to his life than the fire and brimstone of religion. Baldwin grew to believe in the underlying equality of all human beings regardless of the color of their skin or their sexual orientation. His journey to this understanding is what makes the biography the “…Love Story” of Baldwin’s life. Though Lucien and Baldwin remain lifelong friends, Lucien chooses to marry an actress in 1964 which ends Baldwin’s romantic relationship but not Lucien’s outsized influence on his life.
An ironic vignette in Boggs story is Baldwin meeting Richard Wright in America, and later in Paris. Wright’s published book “Native Son” made him famous. “Native Son” is published in the 1940s. The main character in Wright’s book is Bigger Thomas, an impoverished, unemployed, African American, 20-year-old living in a 1930’s Chicago ghetto. He lives with his mother, sister, and brother in a rat infested one room tenement, owned by a wealthy family that is about to offer him a job. Though Baldwin admired Wright’s achievement, he felt “Native Son” identified Bigger Thomas (Wright’s main character) as a symbol of oppression rather than a fully realized human being. This is an interesting insight to what Baldwin does in “Go Tell It on the Mountain”. Baldwin introduces more complexity to the Black experience of life. I’m not sure either Boggs or Baldwin are offering a fair assessment of “Native Son” because Wright clearly shows the environment in which Bigger Thomas lives. Any human being raised in Bigger Thomas’s circumstance is likely to be emotionally challenged and unbalanced.
Richard Wright (Author of “Native Son”)

History shows a rift is created between Wright and Baldwin because of Baldwin’s criticism. To this reader/listener, both are great writers of what is wrong with white or any dominant sexually or racially dominant society.

Baldwin’s abusive domineering stepfather and submissive mother.
Boggs explains why Baldwin’s biography is “A Love Story”. The cruelty of his stepfather drove Baldwin away from belief in God to a love for humanity. One wonders what his stepfather’s cruelty may have had to do with Baldwin’s sexual orientation. The artist, Beaufort Delaney, offers a refuge to Baldwin from his stepfather’s cruelty and helps him reconcile to his sexual identity and a belief in all humans’ equal rights. Lucien helped Baldwin understand love, intimacy, and the equality of human beings. Lucien decides to marry an actress in 1964 but remains a lifelong friend to Baldwin.
Boggs’ biography of Baldwin shows sexual orientation is not, and should never be, a crime. One cannot know what makes a person homosexual, bisexual, asexual, or heterosexual. Bogg’s biography of James Baldwin shows human beings should not be judged by their racial identity or sexual orientation.