Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
The Great Deformation (The Corruption of Capitalism in America)
Author: David Stockman
Narration by: Willaim Hughes

David Stockman (Author, American politician, businessman, and former Director of the Office of Management and Budget for the Reagan Administration.)
David Stockman has written a troubling book about the American economy. Despite his having been an elected representative of Congress and a former Director of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) in the Reagan administration, he argues the fiscal responsibility of America’s government has corrupted “…Capitalism in America”. This is a surprising comment from a former Republican congressman with Republican ties who is a graduate of theological studies, not economics, from Harvard.
Stockton is not educated as an economist. He derides Reagan for profligate spending while having been Reagan’s OMB Director. He feels qualified to argue the crises of 2008 was badly managed because it did not allow the market to allow bankruptcy of major corporations in America. Stockton suggests AIG (American International Group) and the major banking conglomerates of America that have bad debt on their books should file for bankruptcy if they cannot meet their financial obligations without a government bailout. Of course, this is the road not taken so no one can know whether Stockton is right or wrong.


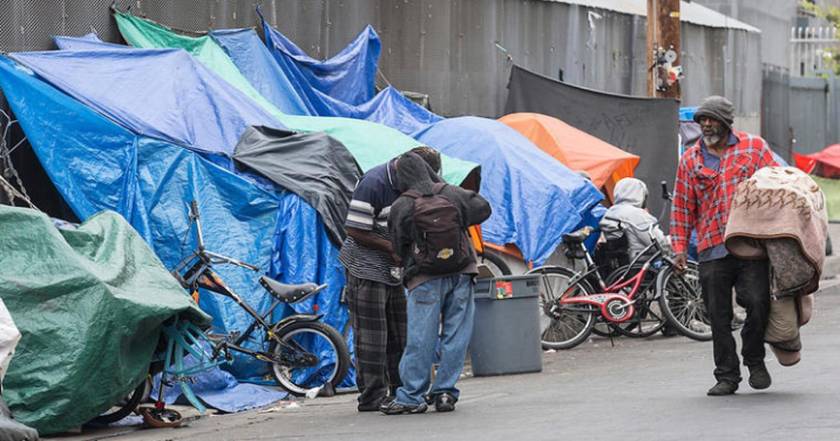
Though the harm done to many Americans by the solution of the Bush’ and Obama’ administrations is fresh in most American’s minds, one cannot help but be skeptical of Stockton’s opinion. If bankruptcy had been allowed by those companies that could not meet their debt obligations, would American capitalism and its economy have been any better? How many Americans would have been harmed by those bankruptcies? The loss of jobs from bankruptcy would have been immense. Consider the number of people with no income who would be unable to pay their bills. What would happen to their ways of life? Would America’s government stand by and allow them to become homeless and hungry? Today’s homelessness suggests America’s government might stand by and do nothing.

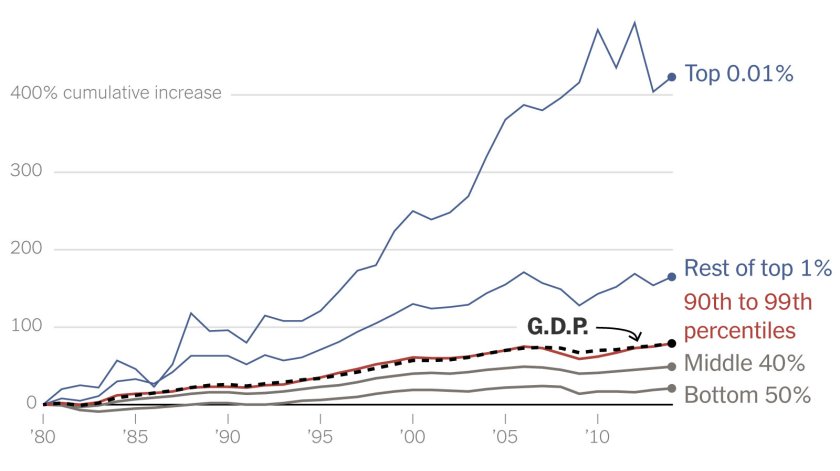
Franklin Roosevelt shows America’s government can finance a solution for crisis through public works that would bring America back to prosperity. Is that different than bailing out employers of the American public to sustain family incomes from a potential financial melt-down. Are the ideals of capitalist greed worth continued impoverishment of the poor?
Stockton’s solution is to cut the defense budget, reduce Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid and let the public fend for itself. Stockton argues to have corporate subsidies and tax expenditures reduced with deep cuts in domestic discretionary spending. He goes on to support binding spending caps, no new tax cuts without an equal offset in expenditures, no bail outs with a belief that nothing is too big to fail, a reversal of Trumps 2017 tax cuts, a balanced budget, no long-term deficit financing, no permanent emergency spending, and a smaller federal footprint on the economy. These seem easy solutions for one who is financially secure but draconian for those who have been unable to grasp the economic opportunities of American capitalism.
More people will die from inability to receive medical care, more will go hungry and suffer from malnutrition, and homelessness. Stockman believes the current system is unsustainable. Let’s accept that point but victimizing and creating more homeless and poorer Americans only cheapens democratic capitalism.
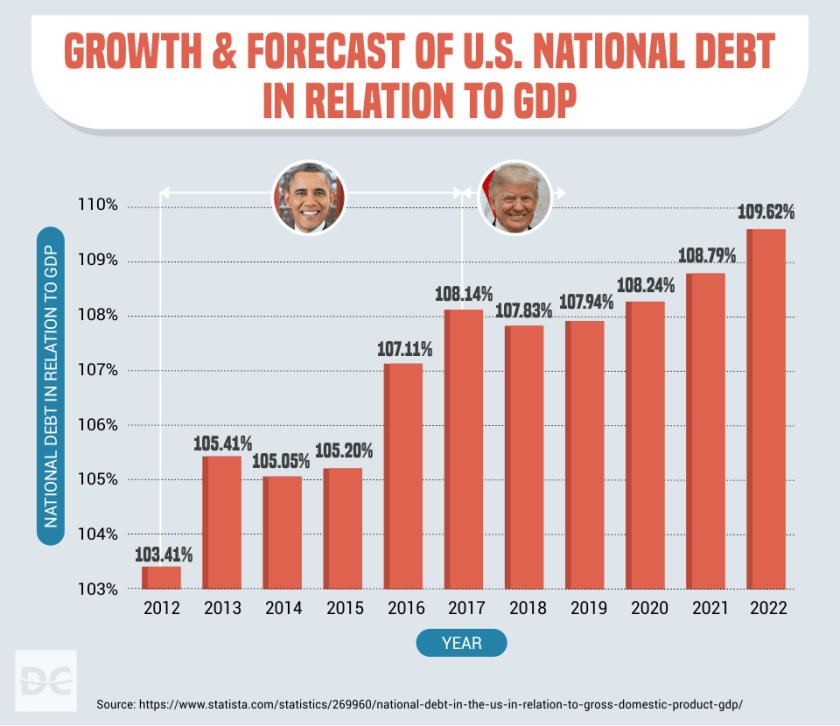
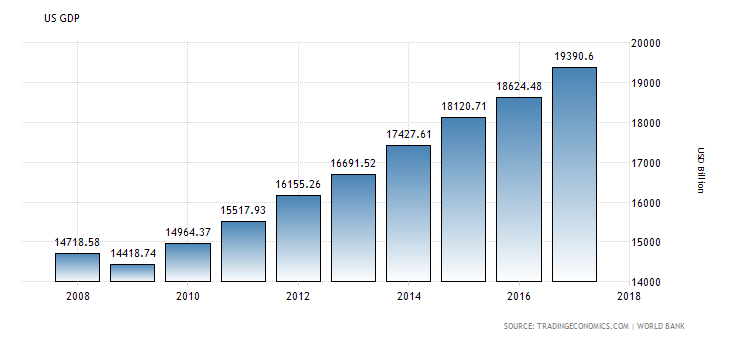
Stockman is right in explaining the U.S. debt increase is unsustainable.
Interest costs are creating extraordinary pressure as a line-item cost for America’s budget. Reform is immensely difficult because of political differences of opinion. According to most economists with education as economists, Stockman’s observations are true, but most economists do not believe that truth will lead to a sudden market collapse. The majority of economist suggest Stockman’s explanation of long-term fiscal challenges can be ameliorated to avoid a wide market collapse. Though Kenneth Rogoff, Carmen Reinhart, and Olivier Blanchard agree with Stockman’s diagnosis, they do not think his doom scenario is likely. Jason Furman, Douglas Elmendorf, and Ben Bernanke do not believe a bond-market revolt will crater government financing. Though all agree government debt is unsustainable, interest costs are rising too fast, and political discord is a problem. These “educated economists” believe entitlements can be gradually reformed, and a sudden collapse of the economy will be abated.




In general, most economists recognize America cannot continue to increase its debt but most economist believe the U.S. will adjust its economic policy to avoid collapse. As a reviewer of “The Great Deformation”, I am personally repelled by Stockman’s analysis but choose to rely on professional economists’ opinion, more than a politician/businessman who had a role in tanking the American economy.