Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
Mother Emanuel (Two Centuries of Race, Resistance, and Forgiveness in One Charleston Church)
Author: Kevin Sack
Narration by: William DeMeritt

Kevin Sack (Author, American journalist, senior reporter for The New York Times who shared a Pulitzer Prize for National Reporting in 2001.)
South Carolina is the underlying subject of Mother Emanuel. It focuses on a State that shows the very best and worst of what it can mean to be born in America. South Carolina is the home of Americans who fought on the side of the confederacy in the Civil War. The confederates of the south did not believe in human equality but in the superiority of the white race and the rightness of slavery.
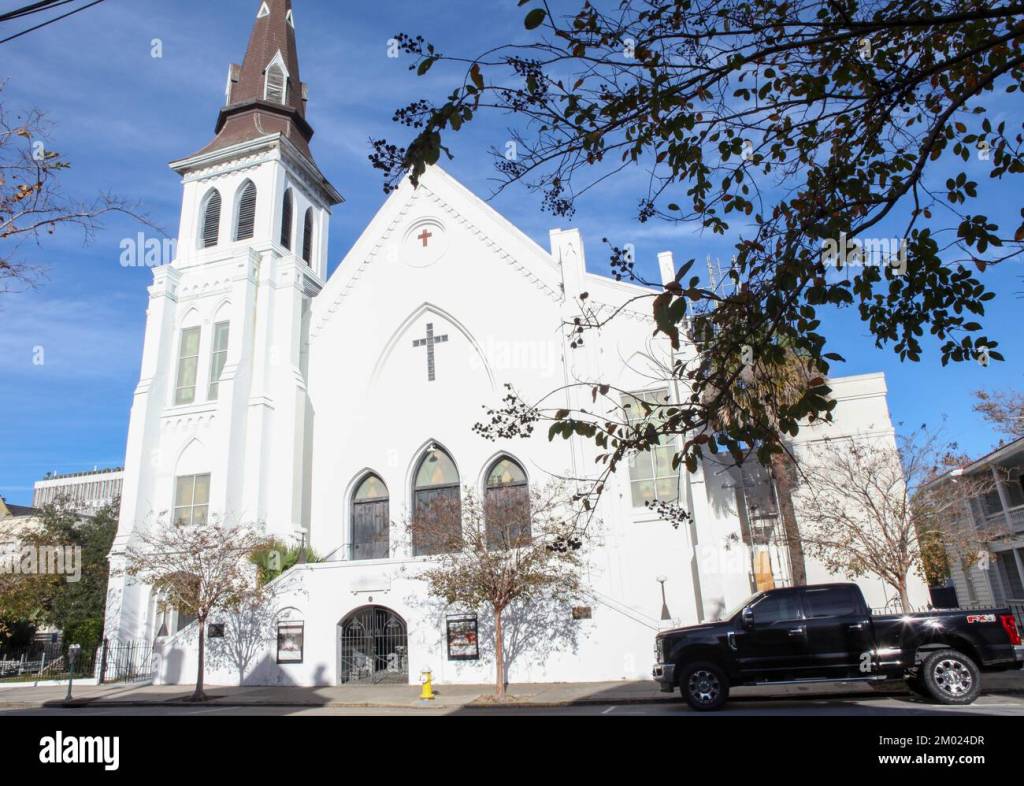

Mother Emanuel is an African Methodist Episcopal Church located at 110 Calhoun Street in Charleston, South Carolina.
Mother Emanuel was built in 1891 and has capacity to seat 2,500 congregates. The church is considered a symbol of Black autonomy and resistance to some South Carolinians. On June 17, 2015, the senior pastor of the church and 8 African American parishioners were shot by a white 21-year-old American name Dylann Storm Roof. Roof, when he came to the church service, is invited into a Bible study group. He sits in the study group for nearly an hour before drawing a 45-caliber Glock handgun to murder 9 people, including the pastor of the church. The author and journalist Kevin Sack explains Dylann Roof was not a dumb white American but a person of above average intelligence who believed Black Americans were an imminent danger to white Americans’ way of life. Roof intended to motivate a Black American uprising that could be crushed by an American white majority.

Dylan Roof (At the time of his trial.)
A listener/reader is unlikely to believe Sack is writing this book to suggest all white Americans, let alone South Carolinians, are like Dylann Roof. Sack is not suggesting all humans have equal capabilities but that all people are influenced by the environment in which they live, their genetic inheritance, and their psychological development. What the author shows is that one’s intelligence can as easily lead to horrific acts of violence, dishonesty, theft, and social hate as belief in the truth of human equality.

Reverend Eric Manning navigated multiple difficulties when he became the pastor of the church after the massacre.
As a church, Mother Emanuel has existed for well over 100 years. It has had many pastors who are subject to the same strengths and weaknesses of all human beings. Sack infers some pastors in Mother Emanuel’s long life have been seduced by the money, power, and prestige of their office while preaching belief in God. Sack infers every human being, including pastors, can be led astray in life. A few, like Dylan Roof, become corrupted by life for reasons that are incomprehensible to one who believes in something greater than themselves, whether that something is the moral, communal, or cosmic reality of human life, or a fervent belief in God and redemption.

Dylan Roof’s verdict for execution is appealed to the U.S. Supreme Court but is rejected. He remains on federal death row.
Dylan Roof is not South Carolina, and neither are the preachers who believe in the divinity and eternity of God. All people of the world are subject to the sins of living life. Roof is shown by Sack to be an unremorseful murderer of human beings for little other reason than the color of their skin. A lesson of life that the murders explain is that forgiveness is not for the sake of Roof’s peace of mind but a mindful reconciliation for those who lost their loved ones.
As of the writing of this book, Dylan roof remains in prison, without personal remorse and a remaining verdict that warrants execution.