Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
The Social Genome: The New Science of Nature and Nurture
By: Dalton Conley
Narrated By: Christopher Douyard

Dalton Clark Conley (Author, Princeton University professor, American sociologist.)
Dalton Conley offers a complex explanation of why one child intellectually and financially excels while others are left behind. The “Social Genome” is an attempt to explain the complexity and inadequacy of genetic research. Not too surprisingly, there seems a correlation between wealth and intellectual development, but its relationship includes familial and environmental nurturing in ways that are too complex for today’s science to measure.
FAMOUS WOMEN IN HISTORY (Many women are as intellectually strong and mentally tough as men, e.g. Cleopatra, Sojourner Truth, Indira Gandhi, Golda Meir, Benazir Bhutto, Malala Yousafzai, and others.)

Dalton argues both genetics and environment shape human intellect and economic success. However, science’s current knowledge of genetic and environmental impact is not clearly understood in a way to aid human development. The current limitations of science make it impossible to determine the precise genetic and environmental factors that shape human development. Dalton offers many examples of how genetics and environment are relevant to human development, but neither are precisely measurable nor manageable.

The idea of clearly understanding the genetic and environmental causes of who humans become is a bit frightening.
Even if it were possible to achieve precise measurement of genetic and environmental influences, should that knowledge be used to create designer human beings?
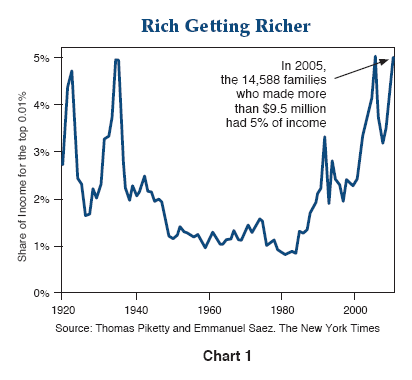
Piketty argues that the income gap widens after World War II. He estimates 60% of 2010’s wealth is held by less than 1% of the population.
Dalton does believe there is a correlation between economic well-being and IQ, but the correlation is affected by genetic inheritance. Dalton concludes economic well-being is a positive factor in IQ improvement. That raises questions about how one can improve the economic well-being of a society to improve IQ. Dalton infers there is no one size fits all solution for IQ improvement. Nurture and nature are too intimately intertwined to know how IQ of a society can be improved. A conclusion one may draw is that environmental and societal factors like human nutrition, general education and improved equal opportunity can mitigate IQ diminishment. Whether one should modify human genomes is a step too far.

In many ways, this is a frustrating book to listen to or read.
If all people looked more alike than different would there be less conflict in the world? No, but being of one race or another makes a difference in one’s opportunities in the world. What is the value of high IQ? If everyone was smarter, would they be happier? It seems the only real value of genetics is in the prevention of known diseases, not in improvement of IQs or creation of a perfect human being (whatever that is).