Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
The Quiet Librarian (A Novel)
Author: Allen Eskens
Narrated By: Livana Muratovic

Allen Eskens (Author, former defense attorney who lives in Minnesota.)
Allen Eskens has written a story of revenge and war without giving it context which diminishes its value. Having visited the former Yugoslavia which is split into 6 ethnic territories, the war that occurred between Bosnian and Serbian people can still be seen in pock marked buildings that were evidence of the war. Our guide for the trip reflects on America and NATO’s failure to aid a peaceful resolution while the conflict killed many people that may have been saved by international intervention. Eskens makes a passing comment about that feeling in his book, but the truth of that conflict is as real today as the people who lived through it.
Josip Broz Tito (Yugoslavian ruler 1953-1980, died in May of 1980.)

When Tito died in 1980, Slobodan Milošević, a nationalist Serbian leader promoted the idea of a “Greater Serbia” without accommodation to ethnic differences of the former Yugoslavian people. Milošević capitalized on the historic conflict between Serb’ and Bosnian’ ethnic and religious beliefs to acquire and hold power. Serbian Christian beliefs were used as a tool to incite support of Milošević’s rule of Bosnians who are generally Muslim believers. Many Bosnians and Serbians die as a result of Milošević. Slobodan Milošević retained power for 13 years but is removed in October of 2000 when Vojislav Koštunica won the presidency. Though Milošević supporters try to protest the election results, they fail.

Slobodan Milošević (President of Serbia 1989-1997, died in 2006 of a heart attack.)
Milošević is arrested in 2001, extradited to The Hague, and tried for war crimes, genocide, and crimes against humanity. He is the first former head of state to be tried by the Hague court. The trial lasted for four years. Milošević is found dead in his prison cell. He was 64. Autopsy shows it to be a heart attack. No verdict is reached, leaving no closure to the victims of his perfidy.
The division of Yugoslavia after Tito’s death.
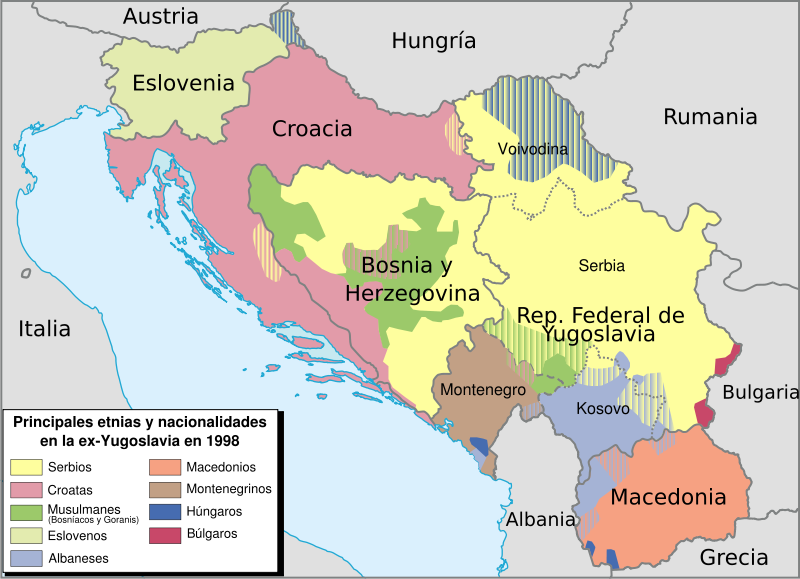
This history does not change Eskens’ story, but it offers context that helps one understand why a Bosnian emigree to America pursued a former Serbian nationalist who brutally raped her mother and murdered her family in front of her during the Bosnian/Serbian war. It is credible fiction of the consequence of war whether in Bosnia or anywhere in the world where the guilty go unpunished. The question becomes, is intent to murder a criminal by one who has firsthand knowledge of another’s heinous act equally guilty of murder? The question is not asked or answered by Esken’s story; probably because it is unanswerable.
The heroine of Eskens story is Hana Babić who emigrates to Minnesota to earn a living as a librarian.
She has adopted the grandson of a close friend who is murdered in the Bosnian/Serbian war. That adoption and her personal experience drives her to find and murder the man who destroyed her life in Bosnia. She has to choose between committing murder in America or letting a murderer go free when she finds her nemesis. However, protecting her adopted boy by letting a guilty person escape vigilante justice is what drives the author’s story. If one sticks with the story, they find her answer.

One wonders about lives of Ukrainians if a tentative settlement proposed by Putin in August 2025 is accepted by Ukraine. Territories under siege in Ukraine would be given to Russia in return for ending the war.
How many Ukrainians will leave their homeland to seek a new life? How many will stay, and secretly fight on? How many will reluctantly accept their homeland’s loss? These were decisions made by Bosnians in former Yugoslavia.
Allen Esken’s story is too tedious and drawn out to be a great work of fiction. However, it reminds one of the injustices of life for those who get away with murder.