Travel
Written by Chet Yarbrough

Mt. Fuji–on our way to Tokyo from Hiroshima, Japan.
Our brief 3-week visit to Japan this year was a pleasant escape from the hostility of a changing immigration policy in America. Our 15-member group of travelers is guided through Japanese culture by three interesting Japanese citizens, i.e. one–a young Japanese student of the piano; two, an American who has lived in Japan for many years, and three, a Japanese’ Hiroshima guide who is an experienced world traveler and guide to her country. All three showed different aspects of a truly fascinating and beautiful country.
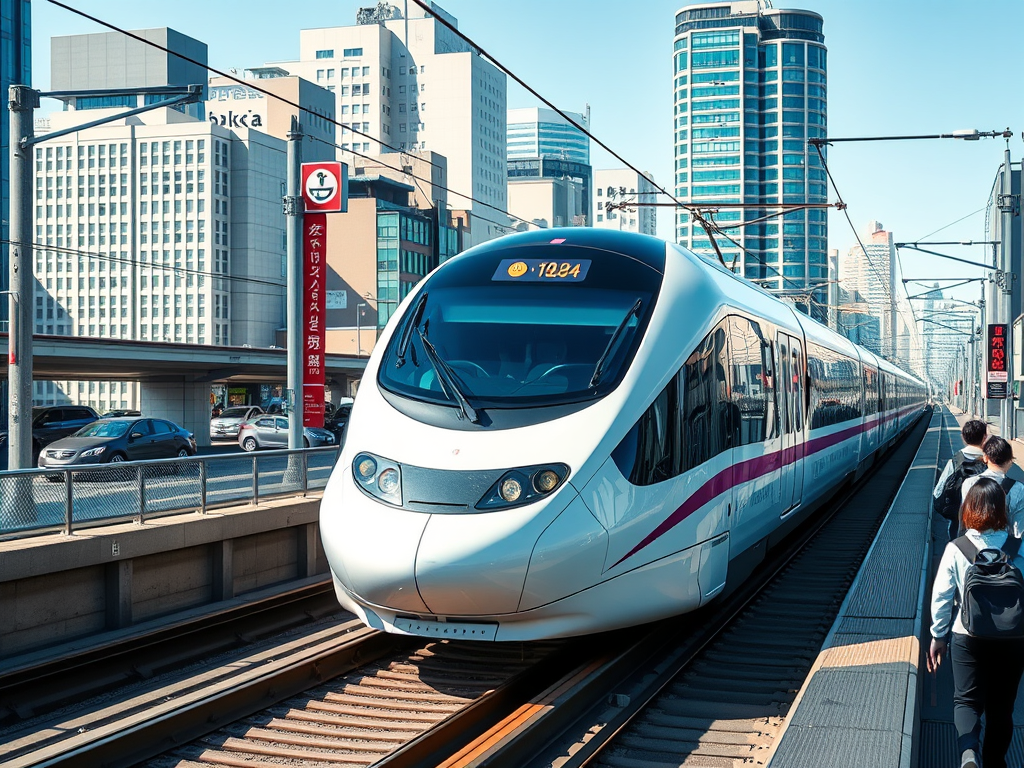

Two of the most striking experiences for me are 1. seeing the incredibly modern infrastructure of Japan and 2. the intelligent use of a densely populated environment. Both of these experiences offer examples to the world of what can be done to accommodate continued population growth. New York City has a population of 8.48 million people while Tokyo’s metropolitan area accommodates 37 million. As an observer of society, my perception is that Tokyo is friendlier, cleaner, and safer than New York City. This is not to disparage New York. New York is one of the greatest entertainment capitols of the world, along with London, but Japan demonstrates how culture makes a difference in how people live.


Tokyo is amazingly clean with shopping for every person’s interest. Shopping centers and markets are busy throughout the metropolitan area. Crowds of buyers are entertained by the appearance of comic figures and pleased to find everything one wishes to buy with a bow of a business employee’s head and a smile of welcome.
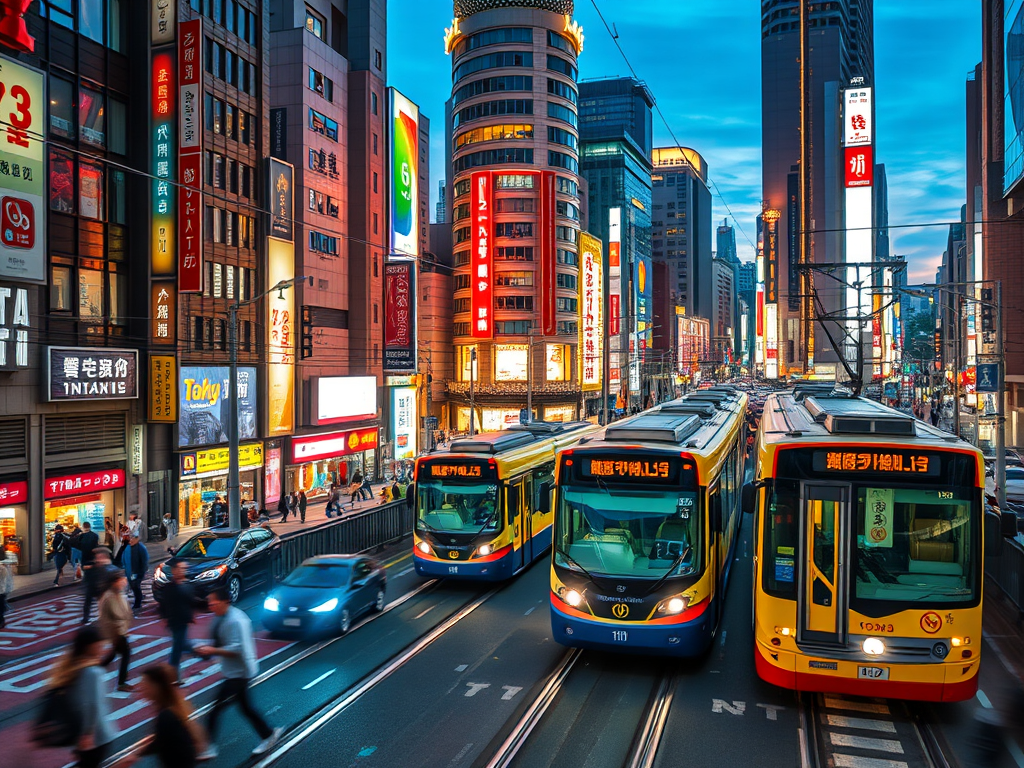

Japan’s public transportation system far exceeds the ease of travel and reliability of New York and other major metropolitan cities in the United States. The highway system and high-speed rail systems of Japan put California’s and America’s fumbling public transportation infrastructure projects to shame.
As an early riser, one can see young women walking by themselves to work in the early morning. They walk down narrow side streets, without concern in Tokyo. In contrast, a woman (let alone a man) is unlikely to feel safe and secure in any of America’s big cities when alone on a street in an early morning or late night.
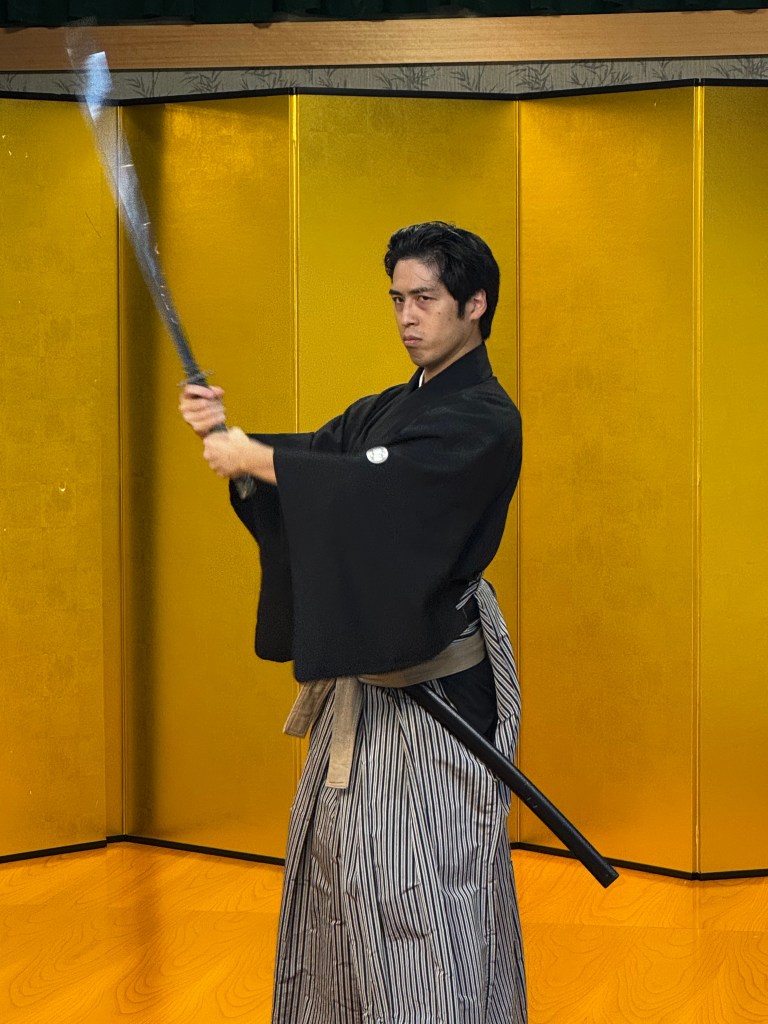

A professional demonstration of Samurai sword tradition is offered our group. After the professional demonstration, my wife demonstrates her skill but has trouble drawing a sword from her belted scabbard, a very funny demonstration for we who were too reserved to participate but entirely willing to laugh.
A home hosted cultural demonstration is given to four of us. Our hosts are a retired Japanese professor and his wife, who is a professional musician. They entertained us for an hour with music and a demonstration of Kabuki theater.
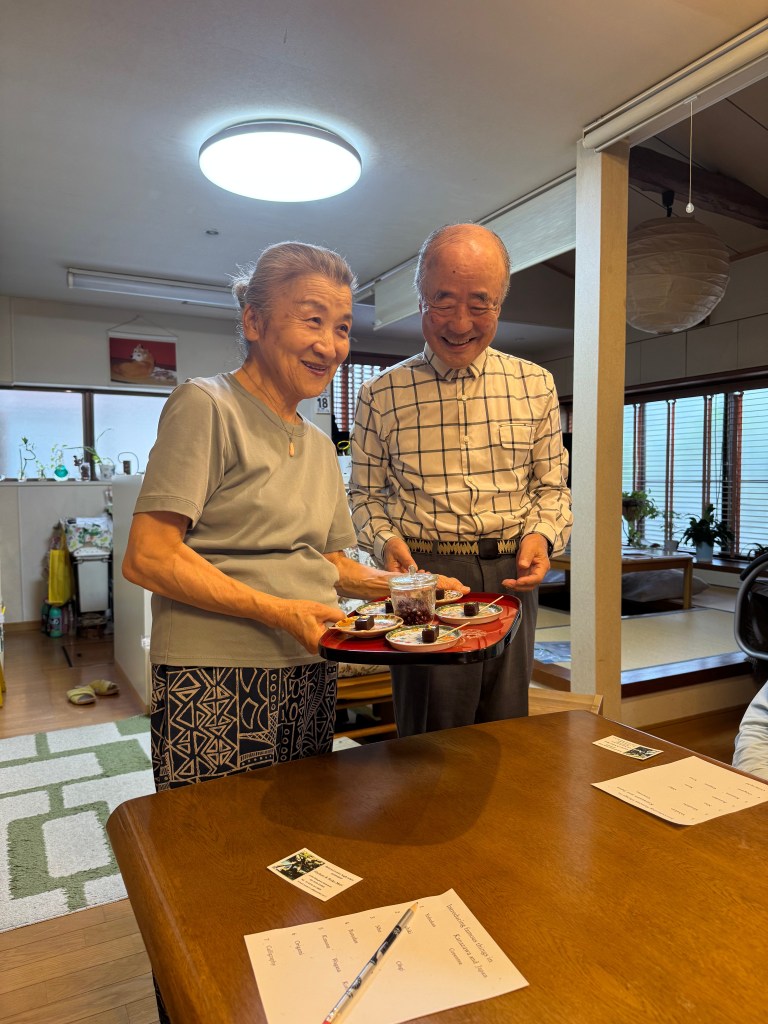

Undoubtedly, there are many Japanese citizens who do not choose to entertain foreign guests but the respect and deference to strangers provided by this couple is a lesson that every American host or hostess could learn when visited by a tourist from another country.

As one travels across Japan, the cities are densely populated but every open space is either bountifully landscaped or prepared for farming or construction.
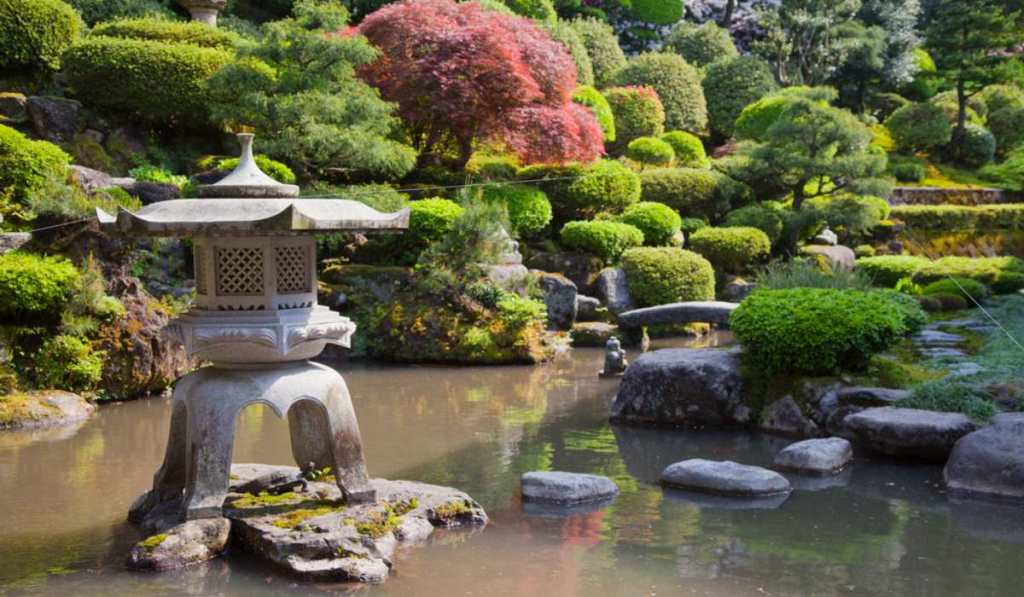
A Japanese garden.
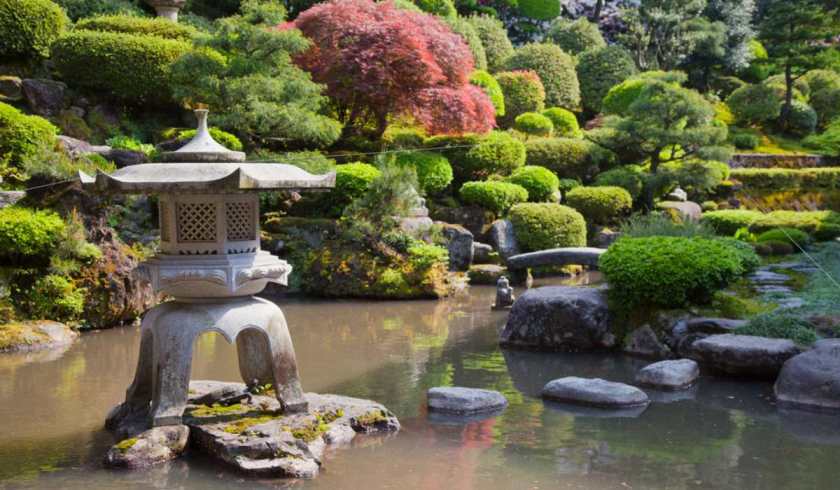

In Japan, there is an obvious effort to create garden areas as a refuge from urbanization. It is as though individual businesses are willing to provide space for mini-New York’ Central Parks to balance nature with urbanization. Travelling across Japan, one can view the care of Japanese forests, garden areas, and open spaces between cities. Highways are designed to minimize noise from automobiles on heavily travelled throughfares.
A park setting and monument to the deadly consequence of the atom bomb that was dropped on Hiroshima in 1945.
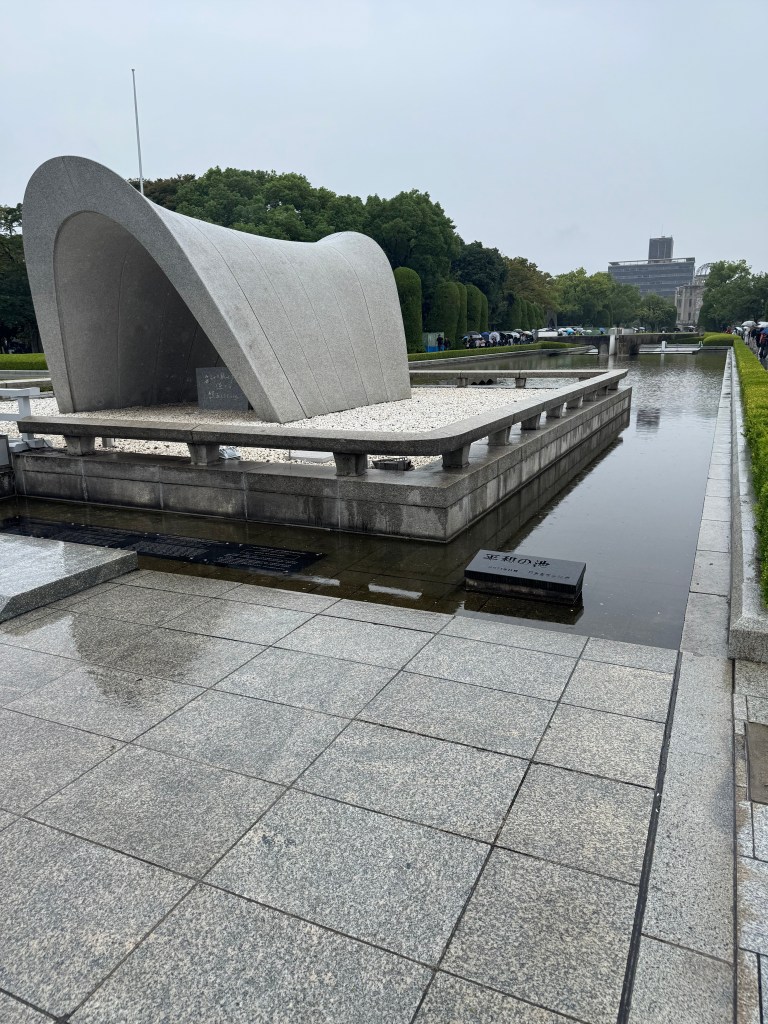

Japan has government policies that keep homelessness invisible by providing housing for the indigent. It is not a perfect system as is noted by one of our guides who explains there is little help to transition the homeless to working lives. Nevertheless, one feels there is a public acceptance of cost for housing of the poor. America could use some of that compassion.

One wonders what makes the difference between cultures. Is it religion? Most Japanese are either Shinto or Buddhist (92.3%). The confluence of these two beliefs is evidence of a common belief that life involves suffering but that everything in nature is a celebration of life rather than preparation for an afterlife. To Japanese, one must have harmony with nature, sincerity, and celebration of life rather than salvation or a beatific afterlife. The Japanese strive to achieve peace within themselves. The ideal is to achieve what is call nirvana, a peace beyond suffering.

I am unsure of the licensing requirements for renting a car in Japan. However, one of our guides advised that he had tried to get a driver’s license twice. He advised the written test is a snap. However, he flunked the driver’s test both times and still has no Japanese driver’s license. After travelling around Japan in taxis and buses, it becomes easy to understand why a driver’s test is so difficult to pass. The roads of Japan are often quite narrow. It is necessary to wait for oncoming traffic before you can proceed. The judgement of a driver is called upon in many narrow road circumstances and only practice reveals the appropriate maneuvers. Added to that complication is the expense of the test when seeking a driver’s license. With a driver test, the cost is $2,000. Traffic is heavy in the major cities and in some rural areas. As a visitor, public transportation is excellent–so considering a car rental is problematic, if not unwise.
Travelling to Japan is an enlightening trip. It may change your life. On the other hand, it may not. It has taken many generations for Japan to become what it is today. By age, America is a baby just learning to walk.
Here’s wishing you a great trip if you choose to go.