Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
Breath (The New Science of the Lost Art)
Author: James Nestor
Narration by: James Nestor

James Nestor (Author, American science journalist.)
“Breath” is a surprising best-selling book about breathing through one’s nose rather than one’s mouth. Nestor’s participation in a 10-day Stanford experiment shows several negative medical symptoms associated with how we breath. Nestor experiences sleep apnea, raised blood pressure, high stress levels, and increased anxiety because of the way he breaths earth’s air. Nextor’s participation in a Stanford University experiment suggests nose breathing is a biological superpower because nasal passages filter and humidify the air we breathe. Exhalation from the way we breath releases nitric oxide and improves oxygen absorption.
Stanford’s experiment reveals CO2 emissions from breathing are essential for all living things.

Experiment shows slow breathing for 5.5 seconds-in, and 5.5 seconds-out improves blood pressure, and heart rate variability that enhances calmness. Surprisingly, slow breathing increases carbon dioxide tolerance while aiding body absorption of oxygen. The consequence of breathing too fast surprisingly impairs oxygen delivery to our system. Oxygen deprivation is one of the causes of anxiety, fatigue, and poor physical performance. Practicing good breathing habits can help reduce anxiety and fatigue to improve physical performance. It is hard to believe changing our breathing habits can have so great an impact on our lives.
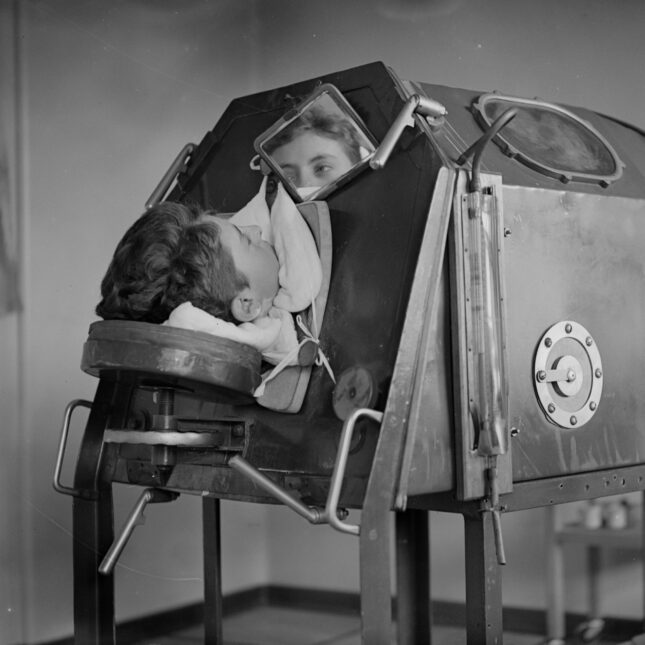

Changing how we breathe is not as easy as one might think.
In the past, when one could not breath on their own, they were placed in an iron tube to replace their natural lung function.
Not breathing through one’s mouth seems an easy change to make in one’s life but a 5.5 second inhale and exhale rule takes practice. The recommendation is to train yourself for 5-to-ten-minute periods until it becomes a learned goal, if not habit. Another suggestion is to alternate nostril breathing by covering one nostril and practicing the 5.5 second inhale/exhale cycle. One can alternate nostrils with breathing in with one nostril and out with the other. Nestor suggests a 4-7-8 technique of breathing. Using only your nose, inhale 4 seconds, hold for 7 seconds, exhale for 8 seconds. He believes it will help one fall asleep if they are having difficulty sleeping. In general, Nestor suggests one should become more aware of how they are breathing during the day.
Dr. Jayakar Nayak (MD, PhD, conducted the breathing experiment as a Professor of Otolaryngology at Stanford University.)

Nestor refers to Dr. Jayakar Nayak’s 10-day Stanford experiment in which Nestor participated. He wrote this book as evidence for the harm he was doing to himself and how mouth breathing for oxygen can be corrected by breathing through one’s nose. Patients, like Nestor, were trained in nose breathing exercises that show marked improvements from the symptoms of sleep apnea, sleep fragmentation, heavy snoring, and stress. Results of the experiment showed sleep apnea and snoring ceased, systolic blood pressure dropped, and heart rate variability improved in most patients who participated in the Stanford experiment.
Nestor’s recommendations are based on nasal breathing, slower breathing, and breath exercises supported by Dr. Nayak’s research. Nestor’s book, “Breath” is worth a reader/listener’s time. Breathing exercises are not a cure-all for sleeplessness, snoring, or regulating blood pressure, but Nestor’s experience and Dr. Nayak’s research encourage reader/listeners to change the way they breath.