Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
Atomic Adventures (Secret Islands, Forgotten N-Rays, and Isotopic Murder-A Journey into the Wild World of Nuclear Science.)
By: James Mahaffey
Narrated By: Keith Sellon-Wright

James Mahaffey (Author, Research scientist at Georgia Tech Research Institute)
“Atomic Adventures” is a reminder of the race for the atomic bomb, its wide pursuit by nations of the world, and research for the holy grail of atomic fusion. Mahaffey’s science explanations are tedious for non-scientists, but his history of the secrets and use of atomic energy are interesting and surprising.

The United States, with the help of the UK, may have been first to acquire the atom bomb in 1945, but eight more nations acquired it by 2006.
United States: Acquired in 1945.
Russia (formerly the Soviet Union): Acquired in 1949.
United Kingdom: Acquired in 1952.
France: Acquired in 1960.
China: Acquired in 1964.
India: Acquired in 1974.
Israel: Believed to have acquired in the late 1960s, though it maintains a policy of deliberate ambiguity.
Pakistan: Acquired in 1998.
North Korea: Acquired in 2006
It is somewhat ironic that Pakistan did not acquire the atom bomb until 1998 when Pakistan’s “father of the bomb”, Abdul Qadeer Khan, became a rich man by selling technological know-how of the bomb to nations like North Korea, Libya, and Iran.

Abdul Qadeer Khan (1936-2021, father of Pakistan’s atomic weapons program, died at age 85.)
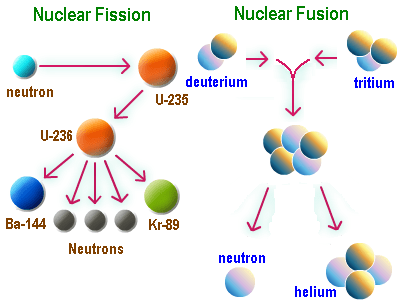
As a singular discovery, Einstein’s E = mc² offered a dual opportunity for the world, i.e., destruction and/or survival of the human race. The bomb suggests destruction while nuclear fusion offers an inexhaustible energy source that could reverse global warming and rocket human beings to other worlds.
ALBERT EINSTEIN (1879-1955, died at age 76.)

Mahaffey explains the immense potential of nuclear power as a principal source of energy. History shows nation-state and political conflicts may spin nuclear power out of control to kill millions and devastate the environment. On the other hand, nuclear research and power offer avenues for humanity’s survival and longevity.
Mahaffey notes there were Japanese, as well as better known German scientists, who were working on the creation of a nuclear bomb that could destroy Allied armaments and combatants. The rush to weaponize radiation during WWII surprisingly includes research being done by Japan as well as Germany during WWII. America won the research race because of superior human and financial resources that could be marshalled to complete the scientific research and experimentation needed to perfect a nuclear weapon.

Mahaffey explores the creation and destructive history of the atom bomb.
Surprising to some listeners, Mahaffey explains Argentina’s significant effort to increase its research and development of nuclear power after WWII. Argentina created the National Atomic Energy Commision in 1950. The chief researcher, hired by President Juan Perón, was Ronald Richter (1909-1991), an Austrian-born scientist who headed their plan to create a fusion power facility. Richter fails but nuclear energy remains an important part of Argentina’s history. In the 1960s they built their own research reactors and by 1974 built their first fission nuclear power reactor, Atucha I. By 1984, they had two heavy-water reactors with Atucha I and Atucha II.
Ronald Richter (1909-1991, Austrian-born German who became an Argentine citizen who headed up the Argentine Huemul Project to create a nuclear fusion power plant. He failed, despite the millions of dollars spent to build and rebuild fusion power plants.

Yoshio Nishina (the father of modern physics research), Bunsaku Arakatsu, and Masatoshi Okochi created the so-called Ni-Go and F-Go projects to develop an atom bomb. They did not get beyond the laboratory stage because of a lack of resources, the exigency of war, and the complexity of nuclear technology. The energy of nuclear power, as shown by history, is two edged.

Yoshio Nishina (1890-1945, the father of modern physics research during WWII.)
On the other nuclear radiation can heal the sick
and potentially provide a clean renewable energy source.

Mahaffey explains how research in fusion can go awry. In a news article, two chemists reported in 1989 that fusion was created in their experiment by involving heavy water (deuterium oxide) and palladium electrodes. They reported excess heat production that they believed was nuclear fusion. As with all scientific experiment, their results had to be confirmed by other scientists testing of their results in the same experiment. Mahaffey, in his role at the Georgia Research Institute, was asked to replicate the experiment. Using the same tabletop experiment, Mahaffey initially confirmed Fleishmann’s and Pons’ findings. However, no other table-top experiments found the same results. What Mahaffey finally found was that the neutron counting device that was recording increased heat was the actual source of the heat increase, not the chemical interaction between heavy water and palladium electrodes. Further research is being conducted but the U.S. Department of Energy concluded in 2004 there is no convincing evidence to support cold fusion. Tests are still being done but Mahaffey infers that research is a scientific dead end. Mahaffey and a colleague tried again in a basement of his colleague’s house to try a similar experiment and failed.

Nuclear power has the potential to revolutionize interplanetary travel. The higher efficiency and power, particularly with the perfection of fusion, will shorten travel times and make trips to Mars and beyond more feasible.
Mahaffey explains how communication will be a challenge when interplanetary travel becomes common. The distance to other planets or galaxies will impede communication because of the limits of the “speed of light”. However, the solution may lie in quantum entanglement’s experimental proof found by Clauser, Aspect, and Zellinger. The complexity of entanglement makes the theory unprovable at the time of Mahaffey’s book.

In theory, quantum entanglement suggests information (communication) may be instantaneously transmitted across galaxies without the limitations of the speed of light.
Mahaffey goes on to explain the risk of radiation in a chapter about a “dirty bomb”. Security measures used to protect the public from radiation leaks make thieves believe something valuable is being secured by government laboratories. Thieves will steal these secure containers only to find they are risking death by opening their booty. Additionally, Mahaffey notes radioactive material is often disposed of illegally and irradiates innocent people who own dump sites that received inadequately contained radioactive material.
Mahaffey is a supporter of nuclear energy and its potential for earth’s energy needs. He argues fission can be made a useful source of energy while fusion research holds the best opportunity for humanity’s future.