Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
“The Rebel’s Clinic” The Revolutionary Lives of Frantz Fanon
By: Adam Shatz
Narrated By: Terrence Kidd

Adam Shatz (Author, editor, professor at Bard College)
Adam Shatz introduces Frantz Fanon to listeners. Fanon was a Black Frenchman, born in the colony of Martinique, an island in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies. Fanon may be classified in many ways but first and foremost one understands he would want to be known as a Frenchman, i.e., a Black individual of French heritage.
Frantz Fanon (1925-1961, graduated from the University of Lyon in France.)

Shatz tells the story of Fanon’s life. Fanon is educated as a psychiatrist who was influenced by Aimé Césaire, a leader of a movement titled Négritude. Négritude was a protest against French colonial rule and assimilation in the early to mid-twentieth century. Fanon lives life by asserting himself as a Black Frenchman with a sense of Black cultural pride.
After an affair with Michele Weyer in college, a daughter is born. The daughter becomes Mirelle Fanon Mendes-France.

Mirelle Fanon Mendes-France (Born in 1948 to Michele Weyer and Frantz Fanon.)
Fanon later marries Marie-Josephe Duble in 1952. Duble was an intellectual, a journalist, and liberation fighter who died in 1989. Fanon and Duble have a son named Olivier who is thought to be engaged with his father’s legacy. Weyer’s and Fanon’s daughter is a scholar and member of the Frantz Fanon Foundation who also works with a United Nations Working Group on African Descent.
Fanon marries a Marie-Josephe Duble. Duble, aka Josie, married Fanon in 1952.

Shatz explains how much more Fanon was than a psychiatrist. Some suggest Fanon was a Marxist because of his anti-colonial beliefs but Fanon’s philosophy extended far beyond Marxist belief in society as an economic class struggle. Fanon was equally concerned about sexism, racism, and colonialism. He embraced a form of humanism. Fannon believed in self-identification as an acculturation process. He considered himself a Black Frenchman, born on a French colonialist island in the West Indies. His life experience as a minority in a colonial country led him to become a practicing psychiatrist in Algeria.
In the 1950s, Algeria was largely populated by Muslim Arabs with a minority of European nationalities.
Arabs in Algeria were poorly treated at a hospital Fanon joined in 1953. He gradually improved their treatment by opening doors to their ethnic identify. Algeria began a fight for independence in 1954. The movement was for social democracy within an Islamic framework that would offer equal citizenship for all citizens of the country. Fanon did not align himself with any religion in what became a violent conflict between French colonization and those who identified themselves as Algerian.
Fanon conflated imperialism and colonialism with racism by institutionalizing control over another based on cultural and/or racial bias.

Shatz shows who Fanon became in the way he treated his patients in Algeria. Fanon argued mentally troubled patients needed to be reconnected to their families and community rather than institutionalized.
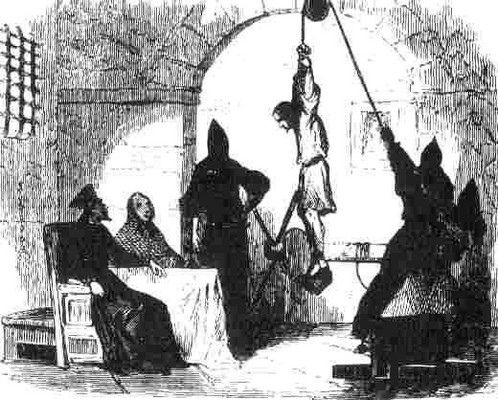

Fanon’s focus was on the psychological impact of human torture and the tit for tat revenge of French occupiers and the Algerian resistance.
Fanon was sympathetic to the Arab desire for freedom and independence for citizens of a country searching for its own identity. Shatz shows Fanon abhorred colonization and its social restrictions. Shatz infers he equally abhorred the revolution’s leaders and followers who tortured and murdered non-combatants, including children. What happened in Algeria reminds one of today’s daily slaughter of children and non-combatants in Ukraine and Gaza.
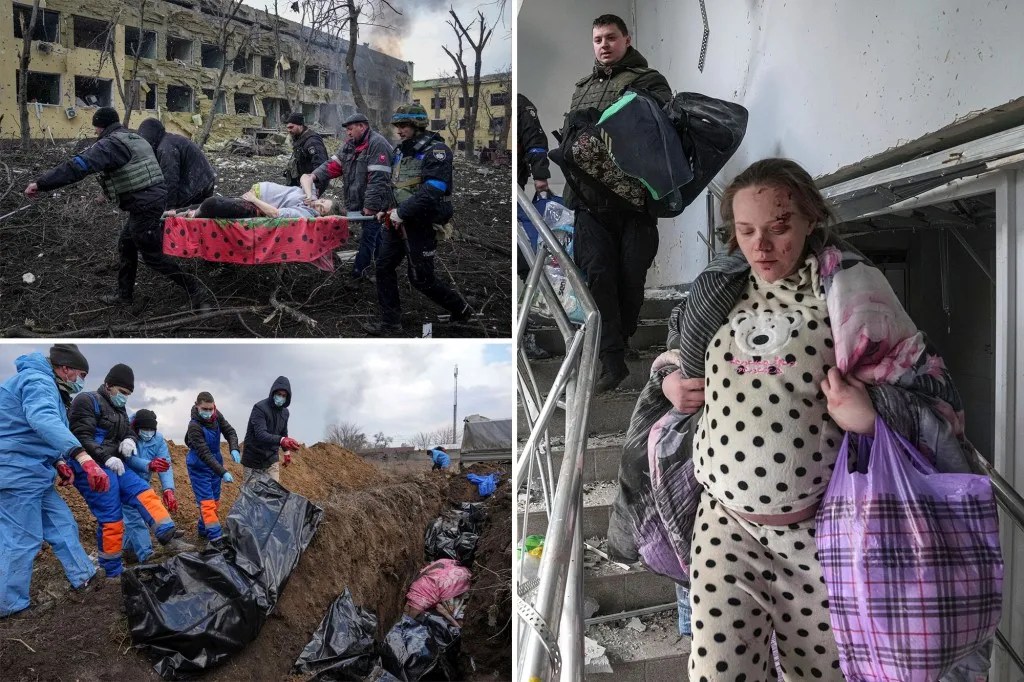


Algeria became an independent nation in 1962 with its own government, culture, and identity. Its ethnic and cultural identity remains the same today as then. It is considered a Muslim country with a majority being Sunni Muslims whose practices play a prominent role in their daily life.
Frantz Fanon dies at the age of 36 from leukemia in 1961, 7 years after the Algerian uprising.

An interesting point in the biography of Fanon is that he recognizes himself as Black in a country that does not commonly describe themselves as people of color but as Algerian Arabs, Berbers, or Europeans. Fanon grows to believe he is Algerian but identifies himself as Black. Black is a broader category of race that makes his story applicable to a wider world but magnifies real-world discrimination based on the color of one’s skin rather than the truth of equal humanness. Of course, as the author notes, the color of skin in Africa is predominantly black and became a frontier for colonization between 1884 and the 1960s.
Shatz infers Fanon fought the good fight. He decried colonization and racism to promote individual dignity and family reconnection in his psychiatric practice. He wrote about and aided people who were different, underserved, and underrepresented. He wrote two books about his life experience to explain why colonialization and racism were culturally wrong and socially destructive. “Black Skin, White Masks” was published in 1952, and “The Wretched of the Earth” in 1961.