Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
1929 (Inside the Greatest Crash in Wall Street History–and How It Shattered a Nation)
Author: Andrew Ross Sorkin
Narration by: Andrew Ross Sorkin

Andrew Sorkin (American author, journalist, and columnist for The New York Times.)
“1929” is a history of the build-up to the stock market crash and the advent of the depression with opinions about how today’s economy compares and what should be done to keep it from happening again. Though Sorkin is not an economist, he has written an interesting history of the build-up to the 1929 depression.

Faltering economies.
There is a sense of danger being felt by some today when reading/listening to Sorkin’s history of the 1920s. Few seem to have a clear understanding of world market forces and whether we are heading for an economic catastrophe or a mere hiccup in the growth of the economy. Neither bankers, regulators, nor politicians in the 1920s (or for that matter now) seem to have a clue about the economy’s trouble and what can be done to ameliorate risks. Like 1929, today’s insiders, power brokers, and rich have more options to protect themselves than most of the world’s population.
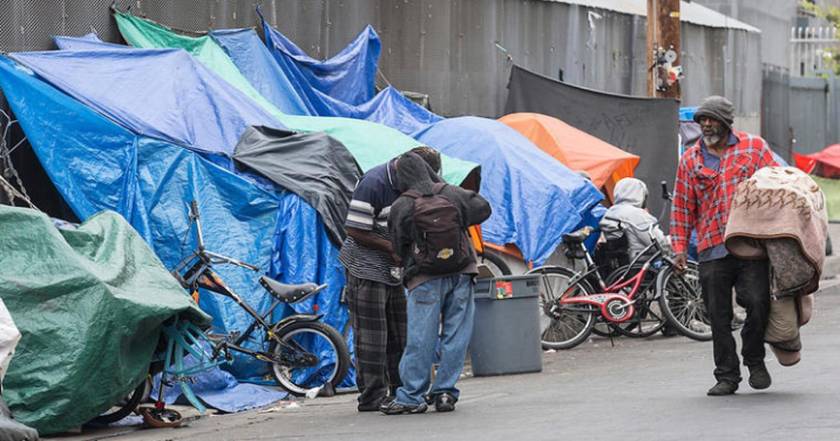

Increasing homelessness in America.
In America, it seems those in power have no concern about the rising gap between rich and poor or the immense increase in homelessness. Without a plan by those in power, there seems little concern about reducing inequality, the common denominator for the wealth gap and homelessness. Sorkin’s book outlines the reality of 1929 that gives reader/listeners a feel of history that may repeat itself.

Sorkin’s history seems credible as he notes human nature does not change.
Today’s leaders are like yesterday’s leaders. Not because they are venal but, like most if not all human beings, leaders in power are concerned about themselves and what there is in life that serves their personal needs and wants. Of course, the difference is that leaders that are power brokers affect others that do not have the same influence or options to protect themselves. We all have blinders that keep us from seeing the world as it is because human nature is to ask what is in it for me, i.e., whatever “it” is. The 1920s had a merger bubble in manufacturing and communication that is fed by the industrial revolution. Today, we have a merger bubble with mega-corporations like Tesla, Apple, Amazon and others that are mega-corporations capitalizing on a new revolution coming with A.I., the equivalent of the Industrial Revolution. Some critics argue mega-corporations, like what happened with the oil industry could be broken up to increase competition which is the hallmark of improved production, cost reduction, and lower consumer prices.

Charles E. Mitchell (American banker, led the First Nation City Bank which became Citibank.)
What makes this history interesting is Sorkin’s identification of the most responsible power brokers who bore responsibility for the stock market crash. Charles Mitchell of Nation City Bank is identified as the central driver of the stock market bubble. Mitchell denied the reality of the financial systems fragility. His ambition and unfounded optimism magnified the systemic risk of the financial crises. He openly defied the Federal Reserve’s warning to curb margin lending that risked other people’s money and their financial stability. He continued to promote purchase of stocks on credit that were fueling the stock market bubble. Mitchell appears to have misled the public in order to increase his power and protect his personal wealth by creating the illusion of market stability and his bank’s profitability. Though Mitchell is not the sole villain, he became the most powerful banker in the nation while breaking the financial backs of many Americans. In general, it is the self-interest of those who listened to him that have responsibility for their financial collapse, but it is always hard to know who is lying to you. Part of the blame is the hesitation of the Federal Reserve Board to act because the people in charge could not agree but that was more a matter of omission than commission which Mitchell was charged with but not convicted. Of course, the political leaders of that time also failed but hindsight is a lot easier than foresight.
Artificial Intelligence is today’s equivalent of the Industrial Revolution of the twentieth century.
Similar to the corporate mergers and investment from growing industrialization of the 1920s, today’s mania is mega corporation’ investment in Artificial Intelligence. Sorkin notes the ease of trading stocks, expectations of crypto investments, and A.I. hype may well move the market beyond its value. He argues for stronger guardrails on speculative investments, more limits on margin lending, and transparency on high-risk investments. He cautions easier credit as seen this Christmas season with buying based on delayed payment incentives and increasing credit card availability, card balance increases, and more liberal repayment terms. In general, Sorkin wants to see more, and better government oversight and regulation of credit offers. He believes too many lenders are overly optimistic about the future with the gap between rich and poor widening and trending to get worse. That inequality threatens the success of capitalism as a driver for shared prosperity, and economic growth.

Herbert Hoover (President 1929-1933, though characterized as the primary villain for the depression, Sorkin identifies his role as one of omission rather than commission.)
The Presidents shown below carry some responsibility for where the American economy is today but that would be another book.




Clinton, the first Bush, the second Bush, Obama, Biden, Trump.
Sorkin’s “1929” makes one think about 20th and 21st century American Presidents who may have set a table for a second economic crisis. As the Turkish proverb says “…fish stinks first at the head.”

