Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
Mother Mary Comes to Me
Author: Arundhati Roy
Narration by: Arundhati Roy
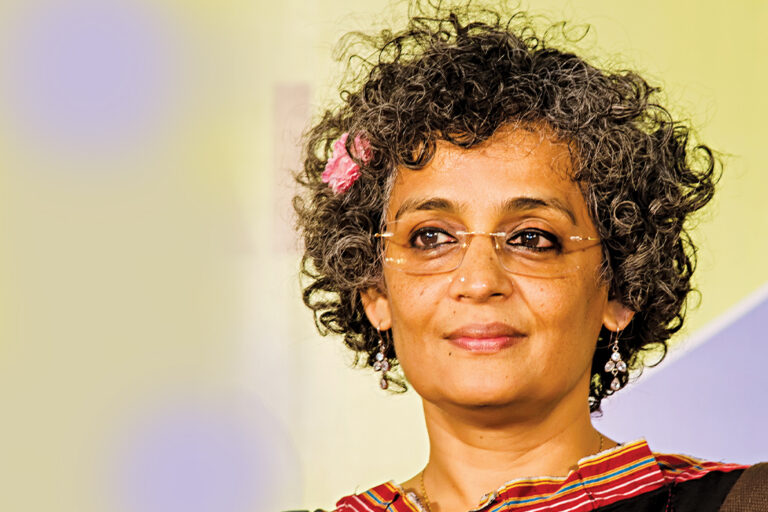

Arundhati Roy (Author, Booker Prize for Fiction awarded in 1997 for “The God of Small Things”.)
Born in India in 1961, Arundhati Roy offers a memoir of her life. Roy is born into a Christian family in a country that is 79.8% Hindu while only 2.3% Christian. Roy suggests her early life is shaped more by instability than penury. Her mother is a teacher who becomes a founder of a school. It seems Roy’s young life is filled with emotional turbulence with a fierce and complicated mother who greatly influences her.
The poverty of India.

The facts of Roy’s memoir are straightforward but the presentation and supporting examples of a mother who is fierce and complicated are both humorous and foreboding. One can understand why Roy is capable of overcoming the hardship of life to become an accomplished writer.

Arundhati Roy’s mother Mary.
Roy explains her mother and father were divorced when she was two years old. Her father was a Bengali Christian who managed a tea plantation but appears absent from most of Roy’s young life. Her mother, Mary Roy, seems a great part of who she became and what she believes. Her mother seems both a source of terror and inspiration. Her mother’s rages and criticism had an immense impact on who Roy became as an adult. Her mother had a reputation as a celebrated educator, and a women’s rights activist who was politically active in Indian rights. Her mother’s education and activism became a gravitational center for Arundhati Roy.
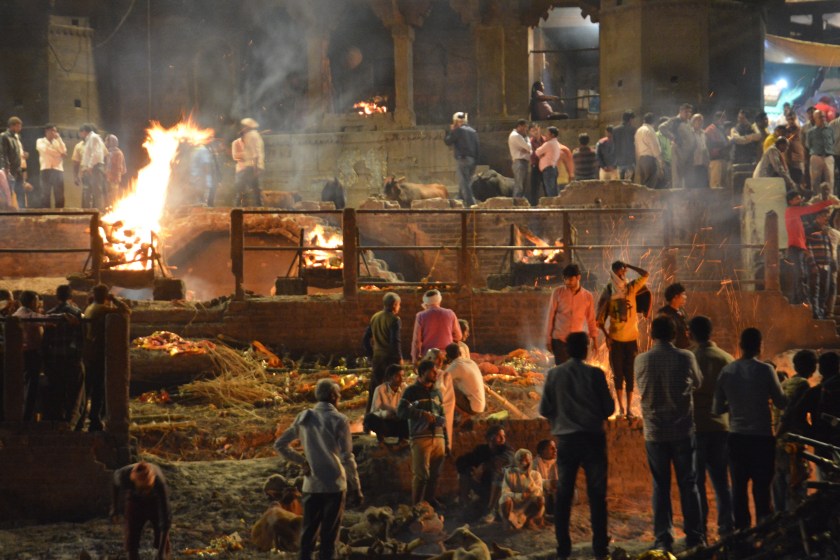

Cremation preparation for burial in the Ganges River in India in 2018.
A part of what makes Roy’s memoir interesting is her perspective on India’s culture. Having traveled to northern India, the harsh climate, overcrowded streets, Ganges burial ceremonies, and obvious poverty juxtaposed with fine hotels and great restaurants is disturbing to a traveler who can afford to see the world.

Single parent homes in America.
However, Roy’s story shows being raised by a single parent (most often a single mother) is not uncommon and the influence of a one parent family appears the same in India as in America. The unique experience Roy has in India is interesting because of its similarity to a single-parent child’s experience in America. Roy is highly influenced by the mother who raised her. Roy is reflecting on truths that apply to children’s experiences in America. Though a single parent to a child is a primary influence, there are others like teachers, mentors, friends, and extended family members that influence who we become. However, being raised by a mother who is responsible for your education and survival tempers your feelings about parenting. You realize how hard a single parent’s life can be with responsibilities beyond taking care of themselves.
A circle of life statue in Norway reflects the importance of mothers in raising children in the world.

Roy, as an adult, recognizes her mother as a sun around which her life revolves. Roy’s mother divorces when Arundhati is two years old. Her father is characterized as an alcoholic and not part of Roy’s life as a child. Her mother is a model of independence, activism, and defiance. Her mother understood, despite male dominance in Indian society, a woman must have grit, political courage, and belief in their role in society. That attitude shaped Roy as a writer and activist. Roy’s mother gave her a sense of self, partly from love but also from respect for independence from the harsh realities of life. Roy’s mother died in 2022 which undoubtedly explains a part of why this memoir is written.

Women’s impact on the world.
Roy explains her mother was intense, intelligent, and emotionally volatile. In Roy’s life, her mother is a source of terror and inspiration. On the one hand, her mother frightened her and her brother but on the other she fueled Roy’s courage and creativity as an independent human being. As she approaches her own adulthood, fear of her mother changes to overt resistance. Roy leaves home at the age of 18 which undoubtedly represents her drive for independence, but she fully realizes her mother’s example made her the adult she became.
Not surprisingly, Roy objects to Hindu authoritarian nationalism represented by India’s political leader, President Narendra Modi.

Roy feels Modi’s BJP party discriminates against women and uses religion as a political tool to weaponize Hindu nationalism that shapes its authoritarianism. She argues dissenters, and minorities are being silenced when seeking equal rights for all. Roy is not writing about her spiritual beliefs but about India’s use of religion, politics, and its legal system to restrict equal rights for all. Roy shows she is her mother’s daughter who is a fierce and opinionated feminist.

Raising children of the world.
In pointing to life in India and Roy’s upbringing, she humorously addresses her mother’s contradictions, her theatricality, and the chaos of her upbringing. What is missing are examples of personal relationships her mother had with others after her divorce from an alcoholic husband. (The truth is that the book is long enough as it is.) Like being raised in India by a single parent, Roy shows parallels of what it’s like to be raised in America. We all become who we are by genetic inheritance, socialization, experience, choice, and chance. It is the parent who stands with us through our childhood that gives us what is good and bad about who we become.
Imagining a single mother raising a child, working full time, and trying to be happy is an arduous task in itself.

Roy’s mother prepared her daughter for the hardship of life with a decent education and the toughness needed to cope with both failure and success. Roy shows her mother succeeded in making her daughter a tough independent adult in “Mother Mary Comes to Me”. Roy’s life seems to repeat some of the mistakes of her mother’s life while forging her own success as a writer and opinionated activist.