Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
Alexander Hamilton
Author: Ron Chernow
Narrated By: Scott Brick

Ron Chernow (Author, biographer of Alexander Hamilton, George Washington, Ulysses Grant, and Mark Twain.)
Though this critic did not care for Chernow’s biography of Washington, his examination of Alexander Hamilton is of some value. Chernow’s attention to detail is impressive. Considering the detail of Chernow’s biographies, it is quite an achievement for Chernow to have had the time to fully research and write histories of one, let alone four, important American’ leaders and influencers.

Traditionally, Alexander Hamilton’s father has been identified as James A. Hamilton, a largely unsuccessful Scottish trader in the British West Indies (approximately 1,000 miles from the American’ continent–made up of the islands of Cuba, Jamaica, and the Lesser Antilles.)
However, Chernow suggests James Hamilton may not have been the father of Alexander because his mother, Rachel Faucette, may have had sexual relations with other men. Ms. Faucette had become James’ lover while being married to Johann Lavien. Faucette had become unhappy and left Lavien in 1750 to take up with James Hamilton. Lavien had Faucette imprisoned for adultery. Lavien eventually divorces Faucette in 1759.
Chernow suggests Faucette, at some point, may have had an affair with Thomas Stevens, a successful merchant and landlord, while living with James Hamilton.

Chernow’s evidence is primarily from reports of Alexander’s close physical appearance to a son of Thomas Stevens. These two young men, Alexander and Thomas Steven’s son, Edward, were about a year apart in age with Edward being the older. Alexander and Edward became close friends, and Thomas Stevens played an important role in Alexander’s life when his mother died. Stevens took Hamilton into his household on St. Croix. Alexander became part of the Stevens’ family.

In Hamilton’s time with the Stevens family, he became educated by reading books and being employed in the mercantile trades of the West Indies.
By any measure, whether Alexander is the son of Stevens or Hamilton makes little difference. By definition, Alexander’s paternity is illegitimate. One asks oneself–so what? Alexander’s genetic inheritance from Faucette and either father leads him to become one of the most important historical influences in the creation of the American Constitution.
Hamilton arrives in New York City in 1772. Hamilton is only 17. The American Constitution is adopted, signed and ratified on September 17, 1787, and implemented on March 4, 1789.


Hamilton’s influence as a representative of New York is to create a centralized government with taxation authority.
This national government is to have the right to enforce national laws that apply to all citizens according to enumerated powers of a federal government under the direction of a President and Congress elected by American citizens. Chernow notes that George Clinton, the governor of New York, is opposed to the strengthening of the federal government because of his interest in maintaining his power as Governor of New York. Hamilton is one of the three representatives of New York at the convention, two of which were opposed to strengthening the federal government.
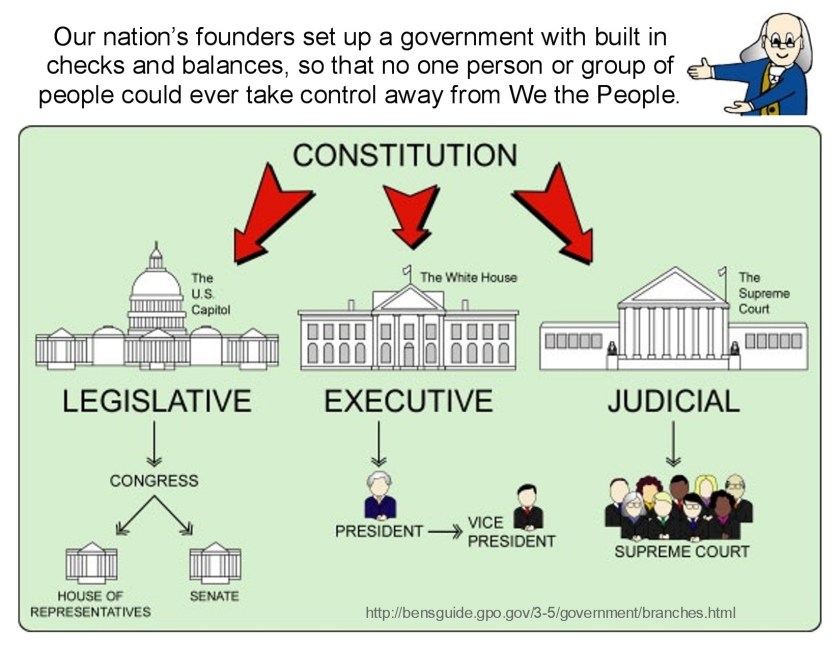
Chernow explains how the convention succeeded in strengthening the federal government.


The two framers that are shown to have the greatest impact on the draft of the Constitution are Alexander Hamilton and James Madison. Chernow explains Hamilton pushed for a strong centralized government with broad powers to tax, regulate commerce, and enforce laws. Madison supports a strong federal government but argues for states’ rights and strict limits on federal authority. Hamilton wishes for broad flexibility for the federal government in the interpretation of implied powers while Madison insists on an explicit statement of the powers of the federal government to limit its implied powers. Hamilton looks to America as an industrializing nation that should be supported by a national bank with federal support for infrastructure improvements while Madison sees America as the agrarian breadbasket for the world with limited banking and industrial’ support by the federal government. Hamilton believes in rule by an educated elite while Madison is concerned about concentration of power in an elitist aristocracy. In the end, Madison takes on the role as the principal author of the Constitution which is intended to limit Hamilton’s expansive interpretation of federal government control of State governance.

It is interesting to be reminded of the danger of a strong executive branch and the consequence of rule by an authoritarian President.
Trump shows loyalty to his beliefs, rather than competence, as the primary qualification for appointment to America’s federal government bureaucracy. Chernow successfully reminds listener/readers of the history of early American government creation, but “Hamilton” is not a page turner like his biography of Mark Twain.

