Blog: awalkingdelight
Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
“American Prometheus” The Triumph and Tragedy of J. Robert Oppenheimer
By: Kai Bird and Martin J. Sherwin
Narrated by: Jeff Cummings


Kai Bird and Martin Sherwin tell the story of America’s “god of fire”. Like the myth of Prometheus who reveals Olympian gods’ knowledge of fire, J. Robert Oppenheimer reveals physicists’ secrets of nuclear fission that give atomic power to humanity. Their history tells listeners of the risk entailed in research and production of nuclear bombs.

J. Robert Oppenheimer (1904-1967, Died at the age of 62.)
Bird and Sherwin offer an intimate and revealing story of J. Robert Oppenheimer that reveals his genius, his human frailty, his growth as a project manager, and the abysmal way American government treated his historic achievements.
Every student of history knows of atomic powers potential to destroy.
Though Bird’s and Sherwin’s history is more about Oppenheimer’s life than his discoveries, it seems prudent to note Oppenheimer discovered the Born-Oppenheimer molecular wave functions about how electrons and positrons work. Oppenheimer also worked with fellow physicist William Phillips on the Oppenheimer-Phillips process in nuclear fusion with work on what is called quantum tunneling. Though Oppenheimer was nominated for a Nobel Prize three times, he never won. Phillips and Steven Chu receive the Nobel in 1997.
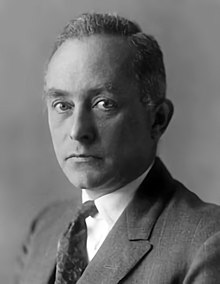

The great controversy surrounding Oppenheimer is his association with communism. Bird and Sherwin clearly acknowledge the association but convincingly argue Oppenheimer was an American patriot who contributed to communist social welfare programs without being a card-carrying member of the CP.
“American Promethius” illustrates Oppenheimer’s growth as a consummate manager of a complex organization that could successfully develop a weapon of mass destruction, an atomic bomb that can end war. However, as history shows, the atom bomb may end a world war, but nuclear bombs become a threat to human existence by any nation that acquires the same technology.

Los Alamos National Laboratory entrance located a short distance NW of Santa Fe, NM
The first atomic bomb exploded on July 16, 1945 in Alamogordo, New Mexico.

The authors show Oppenheimer’s understanding of an atom bomb’s threat by quoting the Bhagavad Gita. “Now I am become Death, the destroyer of worlds.” Oppenheimer refuses to continue research on Edward Teller’s plan to create a fusion bomb of even greater destructive potential. Teller succeeds in creating that bomb. Oppenheimer recognizes any small or large nation that gains fusion bomb technology increases a threat to humanity.

The second atomic bomb test at Bikini Atoll was a fusion bomb released on July 25, 1946. The Marshall Islands, where Bikini is located, is suing the U.S. for what it calls a violation of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
Edward Teller was a leading physicist who worked on the Los Alamos project. Teller’s difficult interpersonal relations and volatile personality made him an important influencer, and defamer of Oppenheimer. Oppenheimer refuses to continue research on a fusion bomb because of its destructive potential and its potential influence in an arms race.
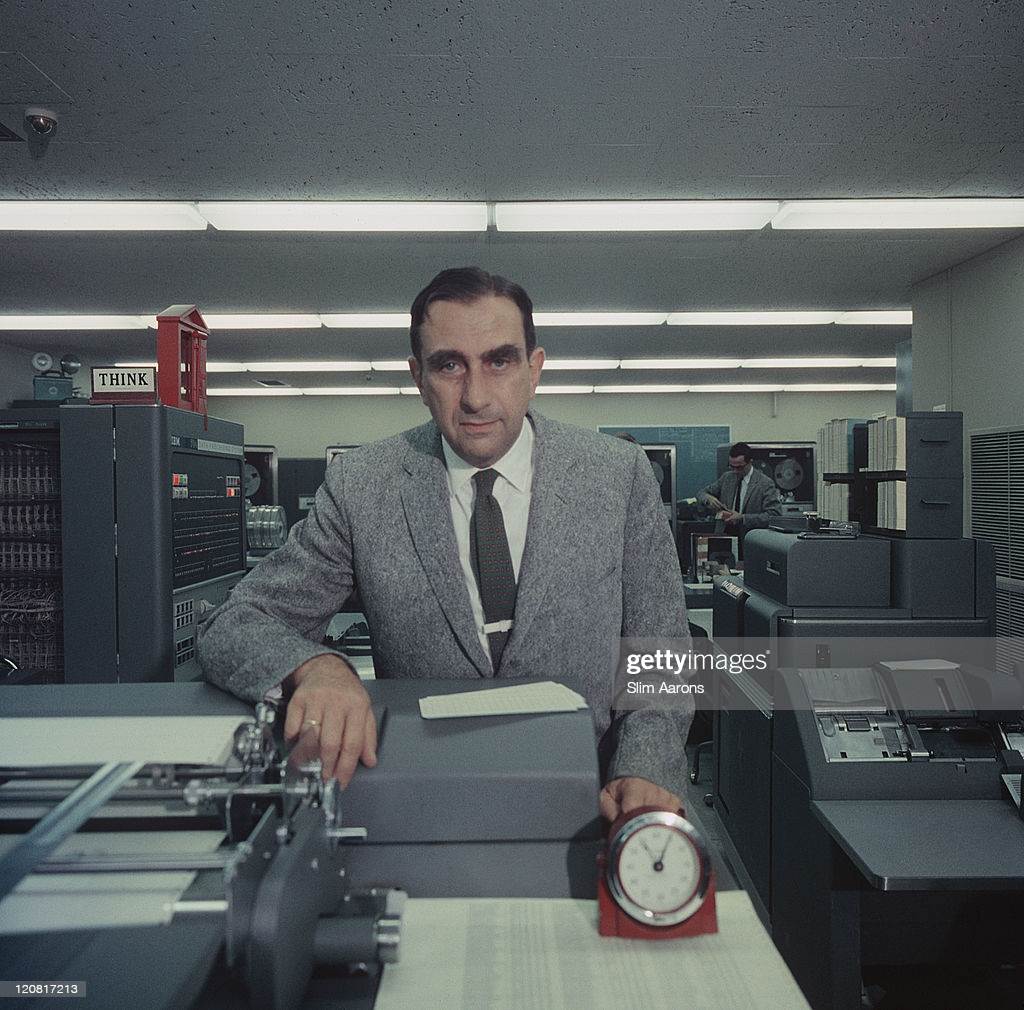

Edward Teller (1908-2003) Hungarian American, theoretical physicist who was the principal inventor of the hydrogen bomb based on the principle of fusion. It’s destructive potential from heat and light are substantially greater than the two nuclear bombs dropped on Japan.)
Teller and an American German physicist, Hans Bethe a team leader, come to lager heads when Bethe agrees with Oppenheimer’s’ focus on a fission rather than fusion bomb. Teller fell out with his team leader, as well as Oppenheimer, over the disagreement.
Hans Bethe (1906-2005, received a Nobel Prize in 1967 for the theory of stellar nucleosynthesis.)
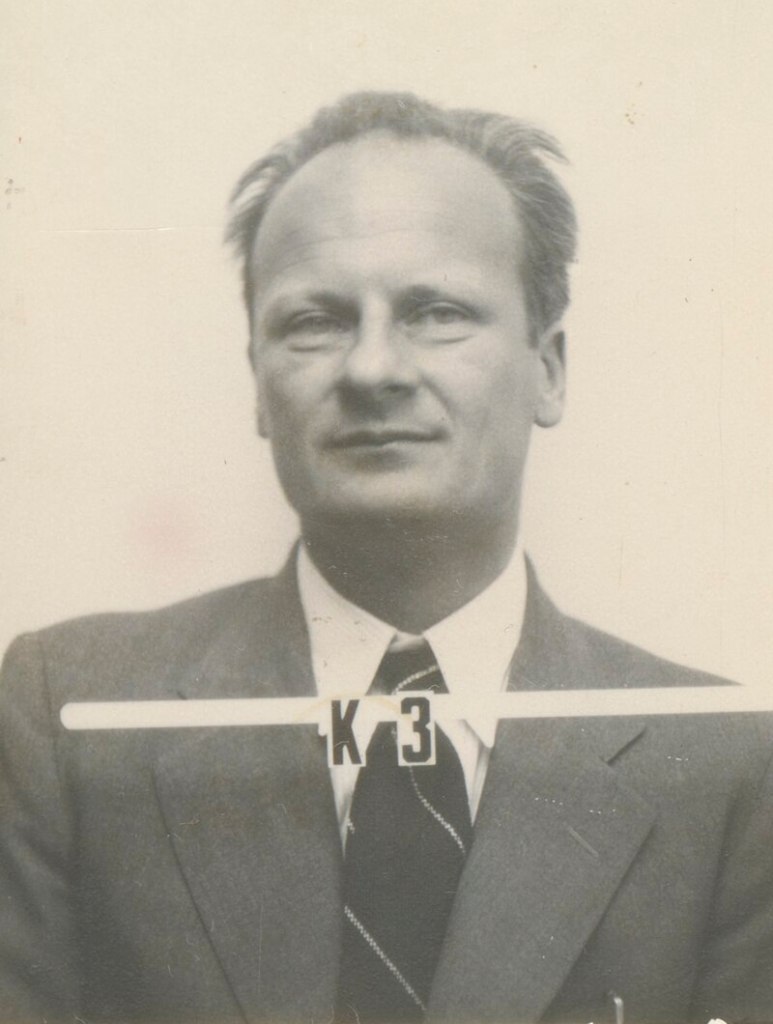


The arrival of Niels Bohr (1885-1962) at Los Alamos in 1943 raises a fundamental concern about creation of a weapon of mass destruction. Bohr’s concern is a nation’s failure to share nuclear physics technology about the bomb with allied forces, particularly Russia, to avoid an international arms race.
Bohr believes scientific cooperation would reduce the probability of an arms race. Bohr’s view seems idealistic in light of today’s history, but the idea is adopted by Oppenheimer. Nuclear weapons have become widely coveted by weaker economic nations of the world because of their political systems failure to improve the lives of their citizens.
Human nature is not overcome by technological sharing because of differences in fundamental religious and political beliefs.

Pursuit of the bomb is just another tool to accelerate national leaders’ political or religious beliefs. Niels Bohr’s noble idea and Oppenheimer’s acknowledgement of the value of sharing science is victim to national leaders’ beliefs and human nature.
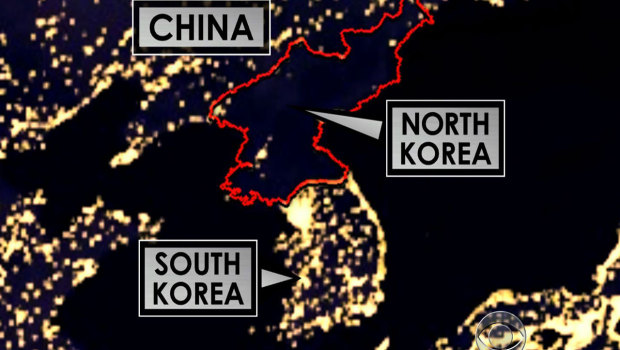
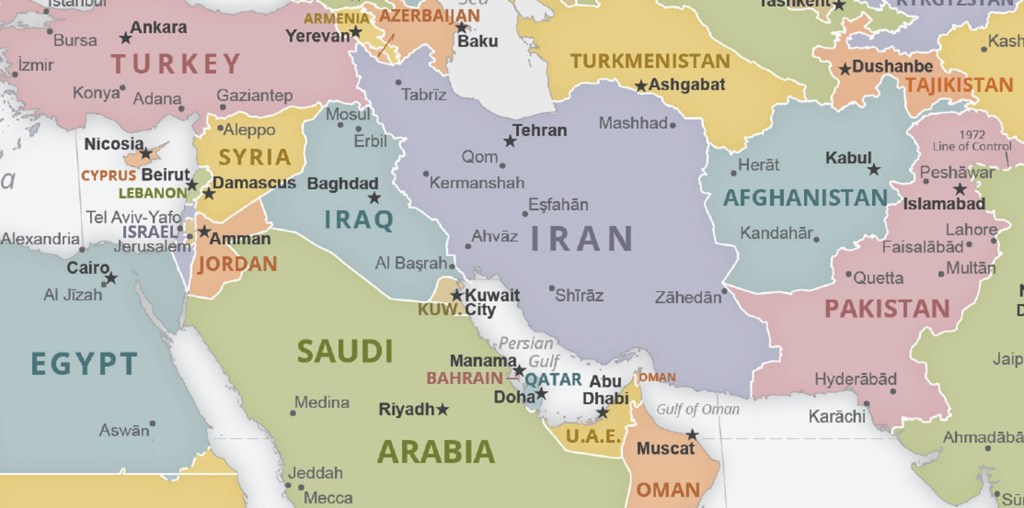
A nation like North Korea covets the bomb because it gives them the ability to punch (negotiate or fight) above their weight. A nation like Iran is led by a religious leader who only views the modern world in light of a beneficent afterlife.

Katherine Oppenheimer. Robert’s wife (1910-1972, German American biologist, botanist, and member of the Communist Party.)
A disturbing note about Oppenheimer is his marriage to his wife, Katherine “Kitty” Puening whom he married in 1940. Kitty became pregnant before they married. They had two children, a boy and girl. This is Kitty’s fourth marriage. Neither parent seems to show much interest in their children. Kitty is shown to be a free spirit, beautiful and charming who generally supports Oppenheimer in his job at Los Alamos. One wonders how their children were affected by their parents’ neglect. Their daughter committed suicide in 1977. The boy still lives in New Mexico and makes a living as a carpenter.

In 1947, Oppenheimer is recruited by Princeton to head a new organization that is called the Institute for Advanced Study. Because of frequent trips to Washington D.C. and the attraction of running a broad organization for the study of science and humanities, Oppenheimer chooses to take the position. His team management experience at Los Alamos and his broad interest in the humanities make Oppenheimer a perfect match for the position. With millions of dollars set aside for the Institute, Oppenheimer attracts the best and brightest science and humanities luminaries from around the world. Einstein, Kurt Godel, John von Neumann, George Kennan, T.S. Eliot, and too many more to mention, were recruited by Oppenheimer. Some were at the height of their professions and became Nobel Prize winners.
The last chapters of “American Prometheus” address the investigation of Oppenheimer’s communist associations during the McCarthy era.

His greatest initial concern was for his brother, Frank, who had joined the communist party. However, the wide range of the investigation and the zealous pursuit of Lewis Strauss, a former shoe salesman who chaired the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC), results in Oppenheimer’s security clearance being stripped. His reputation is unfairly diminished by overzealous politicians and investigators ranging from the FBI director to the AEC chairman.
One leaves this history with a feeling of shame about how Oppenheimer is treated by some and over-praised by others. No human being is without faults, regardless of their intelligence and ability. Oppenheimer was an American patriot who served America with what it needed in the circumstances of his time.

J. Robert Oppenheimer (center) receives the 1963 Enrico Fermi Award from President Lyndon B. Johnson at a White House ceremony on December 2, 1963, as then AEC chairman Glenn Seaborg (left) looks on. (Photo: DOE). He died at age 62 in 1967.
The two edges of nuclear physics that may save or destroy the world is still with us. The best humanity can hope for is balance between human nature and science.



