Books of Interest
Website: chetyarbrough.blog
“Biology: The Science of Life“
Author: Great Book Series
Narrated By: Professor Stephen Nowicki

Stephen Nowicki, Ph.D. (Bass Fellow and Professor of Biology @ Duke University, Associate Chair of the Dept. of Biology and Neuroscience.)
This is a dauting series of lectures with a theory of the beginning of life. It addresses living things in general but more specifically what is known about human life. Not surprisingly, it is immensely complicated.
There may have been an Adam and Eve in history, but Science infers any garden of Eden had to have been long after the beginning of life on earth.

Nowicki explains how Stanley Miller conducted an experiment in 1952 that simulated conditions of the early days of earth’s formation. Methane, ammonia, hydrogen, and water were present in those early days. These ingredients were used in a controlled environment, with the help of energy (primordial lightening), to combine into amino acid compounds that are essential to life. These basic chemicals were present in the early days of earth. These amino acid compounds are the building blocks of life.
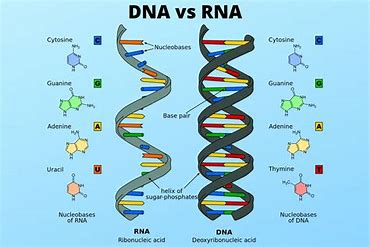
With amino acids, it became possible for DNA and RNA formation. DNA and RNA are shown to synthesize proteins leading to cellular process and organic development.
From these early beginnings, a natural selection process is initialized, i.e. evolution began which led to complex organisms like viruses, bacteria, animals, and eventually humans. Nowicki goes on to explain the complex biology of science. This is a point at which understanding by a lay reader/listener becomes difficult and only partially comprehensible. He begins with a detailed discussion of genetics, the study of genes, their discovery and function.
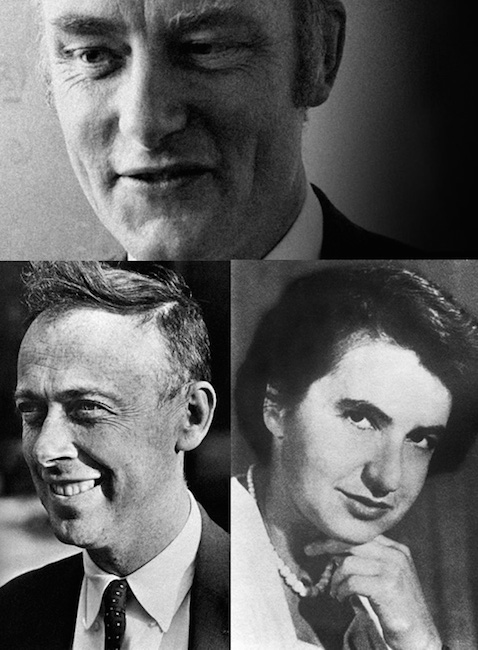
With the help of Rosalind Franklin (lower right), Watson (lower left) and Crick came up with the double helix model made of deoxyribose sugar that alternates with phosphate group strands.

The most famous pioneers of genetics are James Watson and Francis Crick. The genetic model they created reveals the backbone (organizational structure) of genes. With addition of nucleotides (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) to the gene backbone, genetic instructions are encoded by single strands of RNA into double strands of DNA. RNA’s single strands direct ribosomes that prevent mutation and maintain genetic integrity.


Nowicki jumps back in history to explain Darwin’s theory and proof of evolution. In addition, he recounts Gregory Mendel’s discovery of genetic inheritance. (Though Darwin and Mendel were contemporaries, it is not believed they ever met.) Mendel found, in breeding pea plants, that pea plants inherited certain traits of their parent plants with first generation plants having one color flower while second generation had 1/3rd to 2/3rd color differences that experimentally suggest inheritability of appearance. Mendel had no knowledge of genetics but was aware of Darwin’s writing. Ironically, Mendel discovered that inheritance had distinct genetic units of dominant and recessive characteristics explained how second-generation pea plants had mixed colors. This inheritable element of a gene became known as an “allele”, a word coined by British geneticist William Bateson in the early 1900s.

A listener/reader is only 1/4 of the way through Nowicki’s lectures at this point. Many of the remaining lectures delve into the details of gene function that will be interesting to biology students but only confuse and tire a dilettante.
To this reviewer, the two most enlightening features of Nowicki’s lectures are his views on the origin of human life and the ecological loss of biodiversity that threatens human existence. Nowicki challenges religious belief in the origin of life with a convincing argument for nature’s creation of human existence. His last lecture addresses global warming, reduced biodiversity, and the consequences of a loss of earth’s laboratory of medicinal cures for human ailments.
Nowicki leaves listener/readers with belief in humanity’s and earth’s environmental correction but with reservation. Human population growth is slowing, and awareness of biodiversity is improving but is the trajectory of global warming outpacing human action?
